10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(9):3747-3761. doi:10.7150/ijbs.70679 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Repurposing Oxiconazole against Colorectal Cancer via PRDX2-mediated Autophagy Arrest
1. School of Basic Medical Sciences, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, 611137, China.
2. State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center, West China Hospital, West China School of Basic Medical Sciences & Forensic Medicine Sichuan University, and Collaborative Innovation Center for Biotherapy, Chengdu, 610041, China.
3. School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, International Cancer Center, Shenzhen University Health Science Center, Shenzhen 518060, China.
4. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria 3800, Australia.
# These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
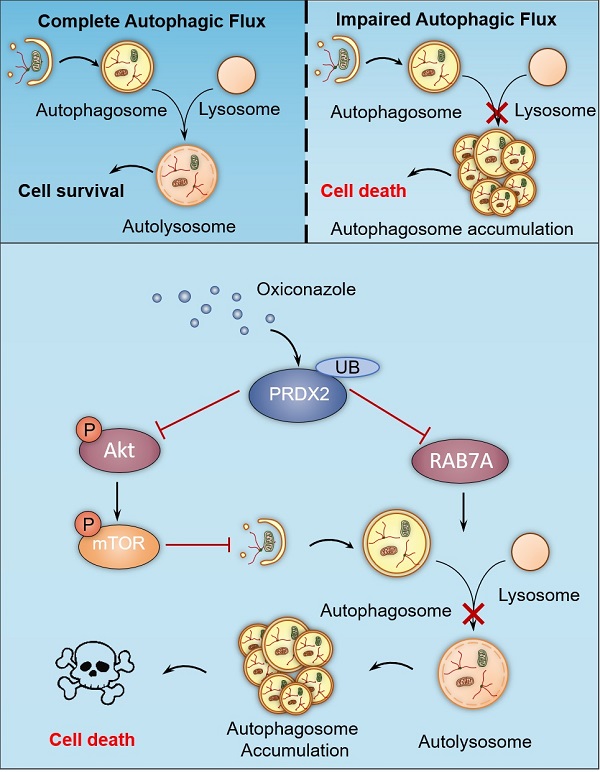
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common malignancies worldwide, yet successful treatment still remains a challenge. In this study, we found that oxiconazole (OXI), a broad-spectrum antifungal agent, exhibits certain anti-tumor effect against CRC. Autophagy arrest and subsequent apoptosis are characterized as pivotal events involving OXI-induced growth suppression of CRC cells. Mechanistically, OXI downregulates the protein levels of peroxiredoxin-2 (PRDX2), an antioxidant enzyme, for reactive oxygen species (ROS) detoxication, to initiate autophagy by inactivating the Akt/mTOR pathway and inhibiting RAB7A-mediated fusion of autophagosome and lysosome, which lead to extreme accumulation of autophagosomes and subsequent growth suppression of CRC cells. Consistently, interfering with autophagy or overexpressing PRDX2 significantly impedes OXI-induced growth suppression of CRC cells. Moreover, OXI plus oxaliplatin, a mainstay drug for CRC treatment, achieves an improved anti-tumor effect. Taken together, our findings bring novel mechanistic insights into OXI-induced autophagy arrest and the growth inhibitory effect on CRC cells, and suggest a promisingly therapeutic role of OXI for CRC treatment.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, oxiconazole, PRDX2, RAB7A, apoptosis, autophagy arrest

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact