ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(9):3908-3917. doi:10.7150/ijbs.71261 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Clinical and biochemical characteristics of 12 Chinese primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy patients with HPGD mutations
1. Shanghai Clinical Research Center of Bone Disease, Department of Osteoporosis and Bone Diseases, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People's Hospital, Shanghai, China.
2. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People's Hospital, Shanghai, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
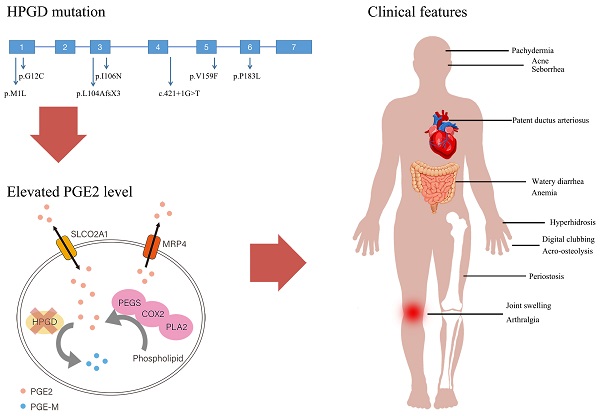
Primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy (PHO) is a rare genetic disease mainly affecting the skeletal and skin. Two genes involved in prostaglandin degradation are known to be responsible for PHO: HPGD and SLCO2A1. HPGD gene mutation can cause PHO autosomal recessive 1 (PHOAR1). The purpose of the present study is to analyze the clinical and biochemical characteristics and HPGD gene mutations of 12 Chinese PHOAR1 patients. Twelve PHOAR1 patients from eleven families, including eleven males and one female, were enrolled in this study. Digital clubbing and periostosis came out to be the most common features, which always occur in the early childhood. We performed HPGD gene analysis and identified six novel (c.1A>G, c.34G>T, c.317T>A, c.475G>T, c.548C>T and c.421+1G>T) and one known (c.310_311delCT) HPGD mutations. The recurrent mutation c.310_311delCT were found in all eleven patients, suggesting it is a hotspot mutation. PHOAR1 patients are considered to have an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. Here, in addition to nine compound heterozygous patients and two homozygous patients, we found one heterozygous patient and reviewed two heterozygous patients reported in other studies. In terms of biochemical characteristics, our PHOAR1 patients have elevated urinary prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) levels (P<0.001) and decreased urinary prostaglandin E metabolite (PGE-M) levels (P=0.04) compared with healthy controls. The patients' PGE2/PGE-M (E/M) ratio came out to be lower than normal subjects (P<0.001). This study provides a comprehensive description of the clinical phenotypes of Chinese PHOAR1 patients and expands the genotypic spectrum of the disease.
Keywords: Primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy autosomal recessive 1, HPGD gene, Clinical manifestation, PGE2

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact