10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(12):4690-4703. doi:10.7150/ijbs.72544 This issue Cite
Review
Friend or Foe? Implication of the autophagy-lysosome pathway in SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19
1. State Key Laboratory of Trauma, Burn and Combined Injury, Institute of Burn Research, Southwest Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing, China
2. Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Macau, Macau, China
3. Chinese Academy of Sciences Key Laboratory of Pathogenic Microbiology and Immunology, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100101 Beijing, China
4. Department of Physiology, School of Preclinical Medicine, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi Province, China
5. Department of Toxicology of School of Public Health, Department of Gynecologic Oncology of Women's Hospital; Department of Central Laboratory, Affiliated Hangzhou First People's Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Abstract
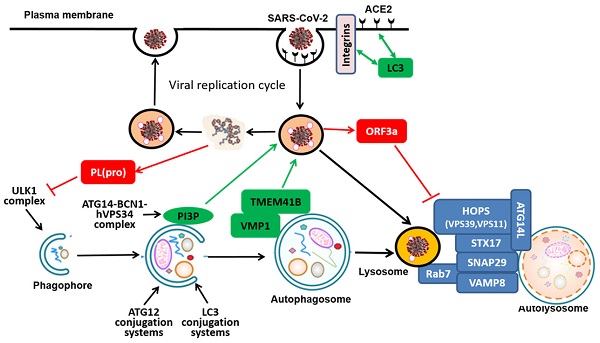
There is increasing amount of evidence indicating the close interplays between the replication cycle of SARS-CoV-2 and the autophagy-lysosome pathway in the host cells. While autophagy machinery is known to either assist or inhibit the viral replication process, the reciprocal effects of the SARS-CoV-2 on the autophagy-lysosome pathway have also been increasingly appreciated. More importantly, despite the disappointing results from the clinical trials of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine in treatment of COVID-19, there is still ongoing effort in discovering new therapeutics targeting the autophagy-lysosome pathway. In this review, we provide an update-to-date summary of the interplays between the autophagy-lysosome pathway in the host cells and the pathogen SARS-CoV-2 at the molecular level, to highlight the prognostic value of autophagy markers in COVID-19 patients and to discuss the potential of developing novel therapeutic strategies for COVID-19 by targeting the autophagy-lysosome pathway. Thus, understanding the nature of such interactions between SARS-CoV-2 and the autophagy-lysosome pathway in the host cells is expected to provide novel strategies in battling against this global pandemic.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2, COVID-19, autophagy, lysosome, clinical trials, therapeutics

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact