ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(7):2727-2747. doi:10.7150/ijbs.90725 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Interstitial Fluid Shear Stress Induces the Synthetic Phenotype Switching of VSMCs to Release Pro-calcified Extracellular Vesicles via EGFR-MAPK-KLF5 Pathway
1. Institute of Biomedical Engineering, West China School of Basic Medical Sciences & Forensic Medicine, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China.
2. Department of Cardiac Surgery, Children's Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, National Clinical Research Center for Child Health, Hangzhou 310052, China.
3. Division of Oral & Craniofacial Health Sciences, Adams School of Dentistry, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, NC, 27599, USA.
4. Department of Genome Sciences, University of Washington, William H. Foege Hall, 3720 15th Ave NE, Seattle 98195, USA.
5. Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, West China Hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China.
6. Department of Cardiology, The Third People's Hospital of Chengdu, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu 610031, China.
7. Key Laboratory for Biorheological Science and Technology of Ministry of Education, State and Local Joint Engineering Laboratory for Vascular Implants, Bioengineering College of Chongqing University, Chongqing 400030, China.
8. JinFeng Laboratory, Chongqing 401329, China.
*These authors contribute equally to this work.
Abstract
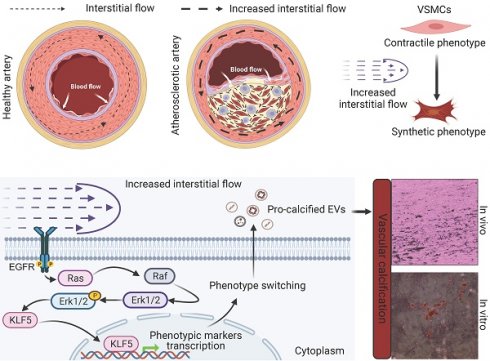
Phenotypic switching (from contractile to synthetic) of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) is essential in the progression of atherosclerosis. The damaged endothelium in the atherosclerotic artery exposes VSMCs to increased interstitial fluid shear stress (IFSS). However, the precise mechanisms by which increased IFSS influences VSMCs phenotypic switching are unrevealed. Here, we employed advanced numerical simulations to calculate IFSS values accurately based on parameters acquired from patient samples. We then carefully investigated the phenotypic switching and extracellular vesicles (EVs) secretion of VSMCs under various IFSS conditions. By employing a comprehensive set of approaches, we found that VSMCs exhibited synthetic phenotype upon atherosclerotic IFSS. This synthetic phenotype is the upstream regulator for the enhanced secretion of pro-calcified EVs. Mechanistically, as a mechanotransducer, the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) initiates the flow-based mechanical cues to MAPK signaling pathway, facilitating the nuclear accumulation of the transcription factor krüppel-like factor 5 (KLF5). Furthermore, pharmacological inhibiting either EGFR or MAPK signaling pathway blocks the nuclear accumulation of KLF5 and finally results in the maintenance of contractile VSMCs even under increased IFSS stimulation. Collectively, targeting this signaling pathway holds potential as a novel therapeutic strategy to inhibit VSMCs phenotypic switching and mitigate the progression of atherosclerosis.
Keywords: phenotype switch, interstitial fluid shear stress, extracellular vesicle, KLF5

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact