10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2015; 11(4):448-455. doi:10.7150/ijbs.11164 This issue Cite
Review
Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 4 in Liver Diseases
1. Department of Infectious Diseases, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034;
2. Department of Oncology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032;
3. Institute of Hypoxic Disease, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069
4. Department of Physiology and Pathophysiology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100069, China.
Abstract
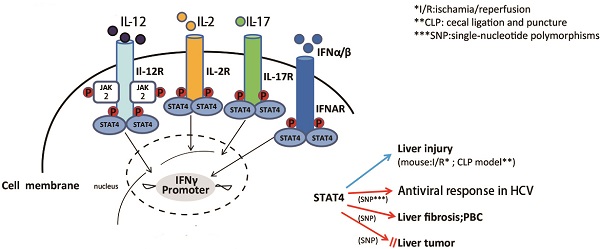
STAT4 is a member of the signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) family of molecules that localizes to the cytoplasm. STAT4 regulates various genes expression as a transcription factor after it is phosphorylated, dimerizes and translocates to the nucleus. STAT4 activation is detected virtually in the liver of several mouse models of liver injury, as well as the human liver of chronic liver diseases. STAT4 gene polymorphism has been shown to be associated with the antiviral response in chronic hepatitis C and drug-induced liver injury (DILI), primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC), HCV-associated liver fibrosis and in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the roles of STAT4 in the pathogeneses of liver diseases are still not understood entirely. This review summarizes the recent advances on the functional roles of STAT4 and its related cytokines in liver diseases, especially in regulating hepatic anti-viral responses, inflammation, proliferation, apoptosis and tumorigenesis. Targeting STAT4 signaling pathway might be a promising strategy in developing therapeutic approaches for treating hepatitis in order to prevent further injury like cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Keywords: STAT4, cytokines, liver injury, chronic hepatitis, liver fibrosis, hepatocellular carcinoma.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact