10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2015; 11(7):825-832. doi:10.7150/ijbs.10861 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Coccomyxa Gloeobotrydiformis Improves Learning and Memory in Intrinsic Aging Rats
1. Department of Pathophysiology, College of Basic Medical Science, China Medical University;
2. Department of Pharmacology, Liaoning Medical University;
3. Department of Urology, the Forth Affiliated Hospital, China Medical University;
4. Tanaka Memorial Laboratory, Nikken Sohonsha Corporation;
5. International Education School, China Medical University;
6. Department of Statistics and Finance, School of Management, University of Science and Technology of China;
7. Department of Ethnopharmacology, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, China Medical University
* Luning Sun and Ying Jin equally contributed at this work.
Abstract
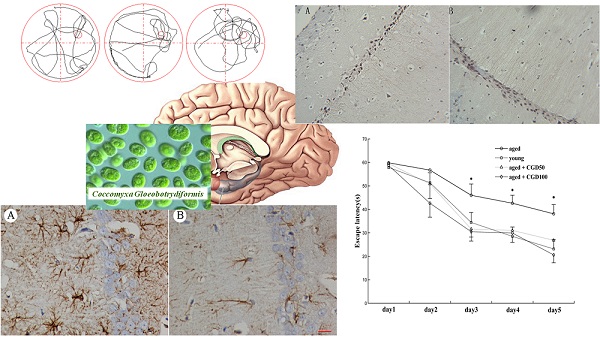
Declining in learning and memory is one of the most common and prominent problems during the aging process. Neurotransmitter changes, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and abnormal signal transduction were considered to participate in this process. In the present study, we examined the effects of Coccomyxa gloeobotrydiformis (CGD) on learning and memory ability of intrinsic aging rats. As a result, CGD treated (50 mg/kg·d or 100 mg/kg ·d for a duration of 8 weeks) 22-month-old male rats, which have shown significant improvement on learning and spatial memory ability compared with control, which was evidently revealed in both the hidden platform tasks and probe trials. The following immunohistochemistry and Western blot experiments suggested that CGD could increase the content of Ach and thereby improve the function of the cholinergic neurons in the hippocampus, and therefore also improving learning and memory ability of the aged rats by acting as an anti-inflammatory agent. The effects of CGD on learning and memory might also have an association with the ERK/CREB signalling. The results above suggest that the naturally made drug CGD may have several great benefit as a multi-target drug in the process of prevention and/or treatment of age-dependent cognitive decline and aging process.
Keywords: Coccomyxa gloeobotrydifomemory, aging, hippocampus, cholinergic neurons, inflammation, ERK/CREB signalling

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact