10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2016; 12(10):1155-1167. doi:10.7150/ijbs.14654 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Class A Scavenger Receptor Exacerbates Osteoclastogenesis by an Interleukin-6-Mediated Mechanism through ERK and JNK Signaling Pathways
1. Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China.
2. Atherosclerosis Research Center, Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Disease and Molecular Intervention, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China.
* SG, YN and JB contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
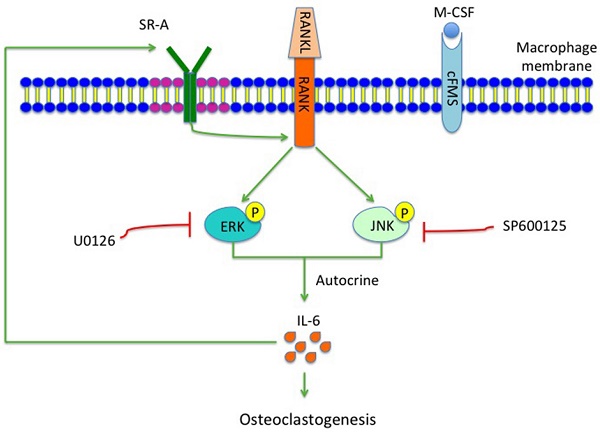
Osteoclasts originate from bone marrow monocyte/macrophage lineage cells, which are important for bone health. Class A scavenger receptor (SR-A) is a multifunctional molecule that functions during differentiation of monocyte into macrophages and osteoclasts. To further characterize the role of SR-A in osteoclasts, we used the murine tooth movement model (TM) and the murine anterior cruciate ligament transection model of osteoarthritis (ACLT OA). In these two models the bones involved are of different origin and have different properties. Bone resorption was decreased in SR-A-/- mice compared to SR-A+/+ mice. Further evaluation showed that the number of multinucleated osteoclasts in SR-A-/- mice, compared to SR-A+/+ mice, was significantly decreased both in vivo and in vitro. The levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6) produced by osteoclasts were reduced in SR-A-/- mice compared to SR-A+/+ mice. In the in vitro marrow-derived osteoclast formation assay and in both mouse models, osteoclastogenesis was restored to normal in SR-A-/- mice by administration of recombinant murine IL-6. Moreover, neutralization of IL-6 reduced the number of osteoclasts formed in SR-A+/+ mice of TM model. Both extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase (JNK), but not p38, signaling pathways were downregulated in receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL)-stimulated SR-A-/- osteoclasts. Importantly, when treated with either ERK or JNK inhibitor, the numbers of osteoclasts generated from RANKL-induced bone marrow derived-macrophages of SR-A+/+ mice, and their IL-6 production, were significantly decreased. This suggests that SR-A activates the ERK and JNK signaling pathways, and promotes production of IL-6 by osteoclasts to further stimulate osteoclast formation.
Keywords: Osteoclasts, SR-A, IL-6, ERK, JNK.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact