10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2016; 12(11):1289-1297. doi:10.7150/ijbs.16405 This issue Cite
Research Paper
P-selectin-mediated LOX expression promotes insulinoma growth in Rip1-Tag2 mice by increasing tissue stiffness
1. Vascular Biology Research Institute, School of Basic Course, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, China
2. Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, the Third Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510630, China
3. Department of Pathology, University of Guangzhou Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510000, China
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
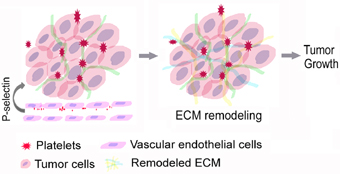
P-selectin, a cell adhesion molecule, is an important member of the selectin family. Recent studies have shown that P-selectin deletion inhibits tumor growth in Rip1-Tag2 mice by suppressing platelet accumulation in tumor tissues. This study aimed to evaluate whether and how P-selectin affects tumor stiffness in Rip1-Tag2 mice. To explore the role of P-selectin in tissue stiffness, we demonstrated that tumor progression in Rip1-Tag2 mice was correlated with tissue stiffness using immunofluorescence and histological staining. Furthermore, we showed that P-selectin deficiency significantly decreased tissue stiffness by inhibiting lysyl oxidase (LOX) expression. Our experiments involving Rip1-Tag2 mice treated with the LOX inhibitor BAPN showed that BAPN significantly abolished collagen deposition to decrease tumor stiffness and thus inhibit tumor growth. These results indicate that P-selectin deletion significantly decreases tumor stiffness in Rip1-Tag2 mice by inhibiting LOX expression. Further study demonstrated that P-selectin-mediated platelet accumulation increases tissue stiffness mainly by increasing LOX expression and thus promotes tumor growth. Therefore, P-selectin may be an effective therapeutic targeting for treating human insulinomas.
Keywords: P-selectin, insulinoma, tissue stiffness, LOX, Rip1-Tag2 mice

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact