10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(1):46-56. doi:10.7150/ijbs.16404 This issue Cite
Review
The Protective Effect of Alpha 7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Activation on Critical Illness and Its Mechanism
1. Trauma Research Center, First Hospital Affiliated to the Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100048, People's Republic of China.
2. Department of Burns and Plastic Surgery, the 181st Hospital of Chinese PLA, Guilin 541002, People's Republic of China.
3. Emergency Department, the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325000, People's Republic of China.
4. State Key Laboratory of Kidney Disease, the Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, People's Republic of China.
Abstract
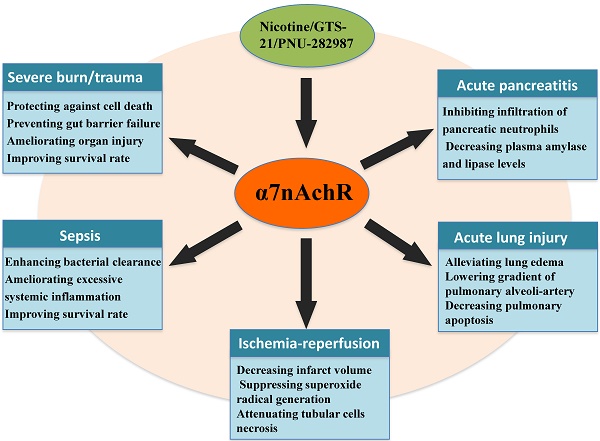
Critical illnesses and injuries are recognized as major threats to human health, and they are usually accompanied by uncontrolled inflammation and dysfunction of immune response. The alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7nAchR), which is a primary receptor of cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway (CAP), exhibits great benefits for critical ill conditions. It is composed of 5 identical α7 subunits that form a central pore with high permeability for calcium. This putative structure is closely associated with its functional states. Activated α7nAChR exhibits extensive anti-inflammatory and immune modulatory reactions, including lowered pro-inflammatory cytokines levels, decreased expressions of chemokines as well as adhesion molecules, and altered differentiation and activation of immune cells, which are important in maintaining immune homeostasis. Well understanding of the effects and mechanisms of α7nAChR will be of great value in exploring effective targets for treating critical diseases.
Keywords: alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, critical illness, cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway, neuroinflammation, immune function, protective effect.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact