10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(1):76-84. doi:10.7150/ijbs.17278 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Inhibition of miRNA-210 reverses nicotine-induced brain hypoxic-ischemic injury in neonatal rats
1. Center for Perinatal Biology, Department of Basic Sciences, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, California, USA.
2. Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai Putuo District People's Hospital, Shanghai, China.
3. Guangdong Cardiovascular Institute, Guangdong General Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China.
Abstract
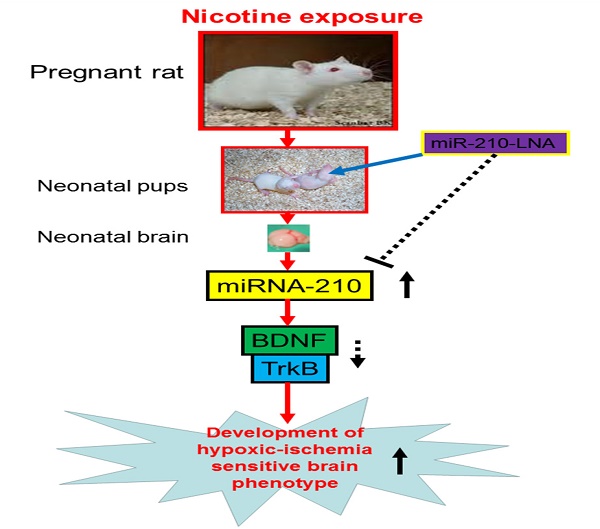
Maternal tobacco use in pregnancy increases the risk of neurodevelopmental disorders and neurobehavioral deficits in postnatal life. The present study tested the hypothesis that perinatal nicotine exposure exacerbated brain vulnerability to hypoxic-ischemic (HI) injury in neonatal rats through up-regulation of miR-210 expression in the developing brain. Nicotine was administered to pregnant rats via subcutaneous osmotic minipumps. Experiments of HI brain injury were performed in 10-day-old pups. Perinatal nicotine treatment significantly decreased neonatal body and brain weights, but increased the brain to body weight ratio. Perinatal nicotine exposure caused a significant increase in HI brain infarct size in the neonates. In addition, nicotine enhanced miR-210 expression and significantly attenuated brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and tropomyosin-related kinase isoform B (TrkB) protein abundance in the brain. Of importance, intracerebroventricular administration of a miR-210 inhibitor (miR-210-LNA) significantly decreased HI-induced brain infarct size and reversed the nicotine-increased vulnerability to brain HI injury in the neonate. Furthermore, miR-210-LNA treatment also reversed nicotine-mediated down-regulation of BDNF and TrkB protein expression in the neonatal brains. These findings provide novel evidence that the increased miR-210 plays a causal role in perinatal nicotine-induced developmental programming of ischemic sensitive phenotype in the brain. It represents a potential novel therapeutic approach for treatment of brain hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in the neonate-induced by fetal stress.
Keywords: perinatal nicotine, microRNA-210, hypoxic-ischemic injury, neonatal brain

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact