10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(2):209-218. doi:10.7150/ijbs.15659 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Increase in Peripheral Blood Intermediate Monocytes is Associated with the Development of Recent-Onset Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Children
1. Key Laboratory of Major Diseases in Children by Ministry of Education, Beijing Children's Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China.
2. Department of Endocrinology, Genetics and Metabolism, Beijing Children's Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China.
3. Laboratory of Immunology, Beijing Pediatric Research Institute, Beijing Children's Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China.
4. Department of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, Beijing Children's Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100045, P.R. China.
*These authors contributed equally to this study.
Abstract
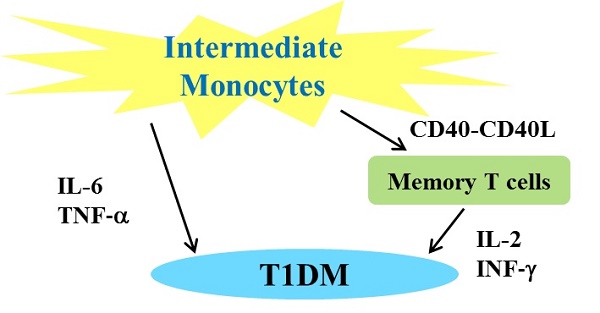
Monocytes play important roles in antigen presentation and cytokine production to achieve a proper immune response, and are therefore largely implicated in the development and progression of autoimmune diseases. The aim of this study was to analyze the change in the intermediate (CD14+CD16+) monocyte subset in children with recent-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and its possible association with clinical parameters reflecting islet β-cell dysfunction. Compared with age- and sex-matched healthy controls, intermediate monocytes were expanded in children with T1DM, which was positively associated with hemoglobin A1C and negatively associated with serum insulin and C-peptide. Interestingly, the intermediate monocytes in T1DM patients expressed higher levels of human leukocyte antigen-DR and CD86, suggesting better antigen presentation capability. Further analysis revealed that the frequency of CD45RO+CD4+ memory T cells was increased in the T1DM patients, and the memory T cell content was well correlated with the increase in intermediate monocytes. These results suggest that expanded intermediate monocytes are a predictive factor for the poor residual islet β-cell function in children with recent-onset T1DM.
Keywords: Children, Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, Intermediate Monocytes, Islet Beta Cell Function, Memory T cells.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact