10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(2):219-231. doi:10.7150/ijbs.16725 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Hyperhomocysteinemia Exacerbates Cisplatin-induced Acute Kidney Injury
1. State Key Laboratory of Organ Failure Research, National Clinical Research Center of Kidney Disease, Division of Nephrology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, P.R. China;
2. Division of Nephrology, Guizhou Provincial People's Hospital, Guizhou Provincial Institute of Nephritic & Urinary Disease, Guiyang, P.R. China.
Abstract
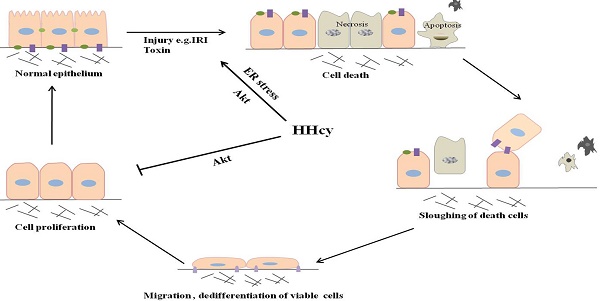
Hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy) has been linked to several clinical manifestations including chronic kidney disease. However, it is not known whether HHcy has a role in the development of acute kidney injury (AKI). In the present study, we reported that HHcy mice developed more severe renal injury after cisplatin injection and ischemia-reperfusion injury shown as more severe renal tubular damage and higher serum creatinine. In response to cisplatin, HHcy mice showed more prevalent tubular cell apoptosis and decreased tubular cell proliferation. Mechanistically, a heightened ER stress and a reduced Akt activity were observed in kidney tissues of HHcy mice after cisplatin injection. Stimulating cultured NRK-52E cells with Hcy significantly increased the fraction of cells in G2/M phase and cell apoptosis together with decreased Akt kinase activity. Akt agonist IGF-1 rescued HHcy-induced cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis. In conclusion, the present study provides evidence that HHcy increases the sensitivity and severity of AKI.
Keywords: Hyperhomocysteinemia, AKI, apoptosis, cell proliferation, ER stress.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact