Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(2):245-253. doi:10.7150/ijbs.16818 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Melatonin Inhibits Glioblastoma Stem-like cells through Suppression of EZH2-NOTCH1 Signaling Axis
1. Department of Neurosurgery, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan 250021, Shandong, China;
2. Department of Neurosurgery, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan 250012, Shandong, China;
3. Department of Histology and Embryology, Shandong University School of Medicine, Jinan, 250012, Shandong, China.
* These authors contributed equally to the study.
Abstract
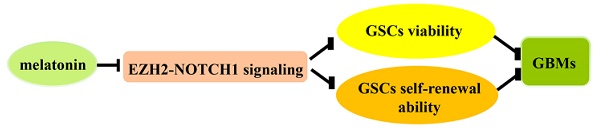
Glioblastoma stem-like cells (GSCs) play essential roles in glioma growth, radio- and chemo-resistance, and recurrence. Elimination of GSCs has therefore become a key strategy and challenge in glioblastoma therapy. Here, we show that melatonin, an indolamine derived from I-tryptophan, significantly inhibited viability and self-renewal ability of GSCs accompanied by a decrease of stem cell markers. We have identified EZH2-NOTCH1 signaling as the key signal pathway that regulated the effects of melatonin in the GSCs. Instead of transcriptionally silencing gene expression by generating a methylated epigenetic mark at histone 3 at lysine 27 (H3K27), EZH2 regulates NOTCH1 expression by directly binding to the NOTCH1 promoter. Moreover, correlation between the expressions of EZH2 and NOTCH intracellular domain 1 (NICD1) was observed in the clinical tumor samples, evidently supporting the existence of EZH2-NOTCH1 interaction in the gliomas and GSCs. Collectively, we demonstrated that melatonin, a potential tumor inhibitor, performs its function partly by suppressing GSC properties through EZH2-NOTCH1 signaling axis.
Keywords: Melatonin, Glioblastoma stem-like cells, viability, self-renewal, EZH2, NOTCH1

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact