10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(4):492-504. doi:10.7150/ijbs.17238 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Deguelin Attenuates Allergic Airway Inflammation via Inhibition of NF-κb Pathway in Mice
1. Department of Respiratory Diseases, The First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China;
2. Department of Respiratory Diseases, Ningbo No.2 hospital, Ningbo, China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
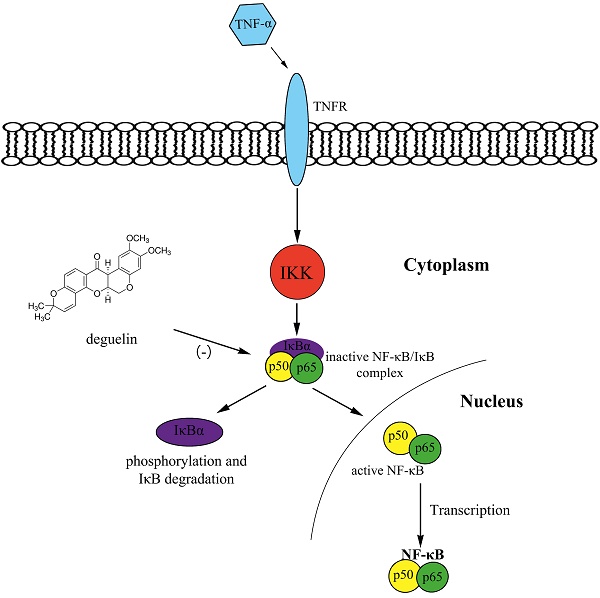
Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by airway inflammation and remodeling, resulting in a substantial economic burden on both patients and society. Deguelin, a constituent of the Leguminosae family, exhibits anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory activities in cancer mice models via inhibiting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases and the NF-κB pathway. We demonstrated that deguelin effectively reduced OVA-induced inflammatory cell recruitment, decreased lung tissue inflammation and mucus production, suppressed airway hyperresponsiveness, and inhibited serum immunoglobulin and Th2 cytokine levels in a dose-dependent manner in asthmatic mice. In addition, we found that deguelin reduced inflammatory gene expressions both in vivo and in vitro, which were closely associated with activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. Thus, we further explored the underlying mechanisms of deguelin in normal human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B). Our results suggested that deguelin inhibited NF-κB binding activity by enhancing the ability of IκBα to maintain NF-κB in an inactive form in the cytoplasm and preventing the TNF-α induced translocation of p65 to the nucleus. In conclusion, our research indicates that deguelin attenuates allergic airway inflammation via inhibition of NF-κB pathway in mice model and may act as a potential therapeutic agent for patients with allergic airway inflammation.
Keywords: Asthma, Deguelin, Inflammation, NF-κB pathway, TSLP.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact