Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(4):505-517. doi:10.7150/ijbs.18834 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Targeting HSP90-HDAC6 Regulating Network Implicates Precision Treatment of Breast Cancer
1. Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Molecular and Medical Biotechnology, College of Life Science, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing 210046, P.R. China;
2. The Key Laboratory of Developmental Genes and Human Disease, Ministry of Education, Institute of Life Science, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, P.R. China;
3. Institute of Immunology and CAS Key Laboratory of Innate Immunity and Chronic Disease, Innovation Center for Cell Biology, School of Life Sciences and Medical Center, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230027, P. R. China;
4. Department of General Surgery, Jinling Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing 210002, P. R. China;
5. Department of Medical Oncology, Jinling Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing 210002, P. R. China;
6. Department of Oncology, Nanjing First Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, 210006, P. R. China;
7. Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Personalized Medicine, Nanjing Medical University, 210006, P. R. China;
8. Cancer Science Institute, National University of Singapore, 14 Medical Drive, 117599, Singapore;
9. Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology, A*STAR, 61 Biopolis Drive, 138673, Singapore;
10. Department of Biochemistry, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, 8 Medical Drive, 117596, Singapore;
11. Co-Innovation Center of Neuroregeneration, Nantong University, Nantong 226001, China;
12. Jiangsu Provincial Clinical Key Discipline and Laboratory of Otology, Nanjing 210008, China.
* These authors contribute equally to this work.
Abstract
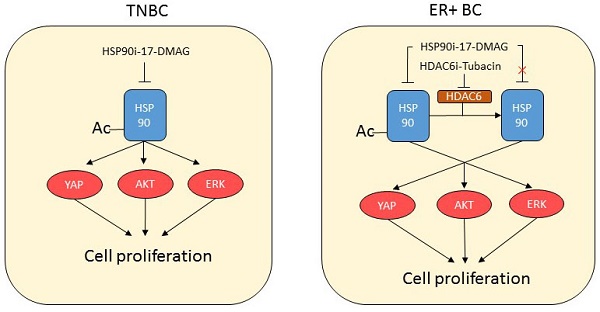
Breast cancer is the leading cause of women death. Heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) and Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) are promising anti-cancer drug targets. However, it's still unclear the applicability of anti-HSP90 and anti-HDAC6 strategies in precision treatment of breast cancer. In current study, we found that triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells, compared to T47D, an ERα+ breast cancer cell line, exhibited 7~40 times lower IC50 values, stronger cell cycle perturbation, increased cell apoptosis and stronger inhibition of cell migration upon 17-DMAG treatment, while T47D, compared to TNBC cells, expressed higher HDAC6 and showed stronger anti-cancer response upon treatment of Tubacin. Mechanically, 17-DMAG treatment inhibited a complex network consists at least ERK, AKT, and Hippo pathway in TNBC cells, and higher expression of HDAC6 inhibited HSP90 activity via deacetylating HSP90. Furthermore, we found higher HDAC6 expression level in tamoxifen-resistance T47D than that in T47D, and Tubacin treatment suppressed the growth of tamoxifen-resistant cells in vivo. Our data suggested that anti-HSP90 and anti-HDAC6 are promising strategies to treat TNBC and ERα+ breast cancers respectively, and anti-HDAC6 can be considered during treatment of tamoxifen-resistance breast cancers.
Keywords: Breast cancer, TNBC, HSP90, HDAC6, tamoxifen resistance.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact