10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(5):652-659. doi:10.7150/ijbs.19108 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Ezh2 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Kras-driven Lung Adenocarcinoma
1. E-institutes of Shanghai Universities, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Proteomics, Genetic Laboratory of Development and Disease, Institute of Biotechnology, Beijing 100071, China.
Abstract
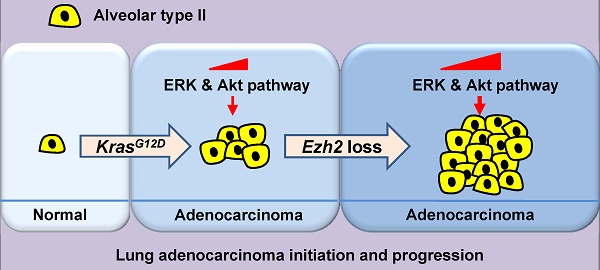
Previous studies have suggested that enhancer zeste homolog 2 (Ezh2), a histone methyltransferase subunit of polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2), acts as an oncogene in lung adenocarcinoma (ADC) development. However, we found that in human lung ADC samples, deletion and mutations of EZH2 were also frequently present, with 14% of patients harboring loss-of-function EZH2 alterations. To explore the effect of Ezh2 loss on lung tumor formation, lung epithelial Ezh2 gene was deleted in Kras-driven lung ADC mouse model. Unexpectedly, Ezh2 loss dramatically promoted Kras-driven ADC formation. KrasG12D/+;Ezh2fl/fl mice exhibited shorter lifespan, more tumor lesions and higher tumor burden than KrasG12D/+ mice, suggesting the tumor-suppressive role of Ezh2 in Kras-driven ADCs. Mechanistically, Ezh2 loss amplified Akt and ERK activation through de-repressing its target insulin-like growth factor 1 (Igf1). Additionally, Ezh2 loss cooperated with Kras mutation to exacerbate the inflammatory response, as shown by massive macrophage and neutrophil infiltrates, as well as a marked increase in tumor-associated cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α. Taken together, our findings revealed the tumor suppressive function of Ezh2 in Kras-driven ADCs, underlining the importance of revaluating the application of EZH2 inhibitors in a variety of cancers.
Keywords: Ezh2, tumor suppressor, Kras, lung adenocarcinoma.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact