10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(6):772-781. doi:10.7150/ijbs.19603 This issue Cite
Review
Angiomotin Family Members: Oncogenes or Tumor Suppressors?
1. Department of Oncology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xian Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi Province ,710061, P.R. China;
2. Center for Translational Medicine, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xian Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi 710061, P.R. China.
Abstract
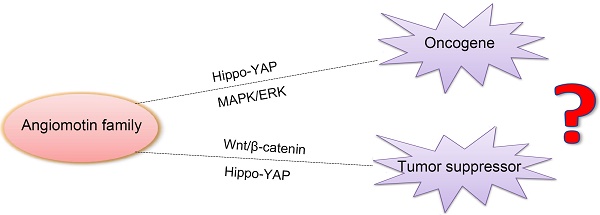
Angiomotin (Amot) family contains three members: Amot (p80 and p130 isoforms), Amot-like protein 1 (Amotl1), and Amot-like protein 2 (Amotl2). Amot proteins play an important role in tube formation and migration of endothelial cells and the regulation of tight junctions, polarity, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in epithelial cells. Moreover, these proteins regulate the proliferation and migration of cancer cells. In most cancers, Amot family members promote the proliferation and invasion of cancer cells, including breast cancer, osteosarcoma, colon cancer, prostate cancer, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, cervical cancer, liver cancer, and renal cell cancer. However, in glioblastoma, ovarian cancer, and lung cancer, Amot inhibits the growth of cancer cells. In addition, there are controversies on the regulation of Yes-associated protein (YAP) by Amot. Amot promotes either the internalization of YAP into the nucleus or the retention of YAP in the cytoplasm of different cell types. Moreover, Amot regulates the AMPK, mTOR, Wnt, and MAPK signaling pathways. However, it is unclear whether Amot is an oncogene or a tumor suppressor gene in different cellular processes. This review focuses on the multifunctional roles of Amot in cancers.
Keywords: Angiomotin, cancer, oncogene, tumor suppressor, YAP.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact