10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(10):1276-1286. doi:10.7150/ijbs.19531 This issue Cite
Review
Pathogenic Role of Exosomes in Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-Associated Cancers
1. Sunway Institute for Healthcare Development (SIHD), Sunway University, Jalan Universiti, Bandar Sunway, 47500 Subang Jaya, Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia.
2. Molecular Pathology Unit, Cancer Research Centre (CaRC), Institute for Medical Research (IMR), Jalan Pahang, 50588 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
3. Institute for Research, Development and Innovation, International Medical University (IMU), Jalan Jalil Perkasa 19, Bukit Jalil, 57000 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
4. Anatomical Pathology Department, Sunway Medical Centre, Jalan Lagoon Selatan, Bandar Sunway, 47500 Subang Jaya, Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia.
Abstract
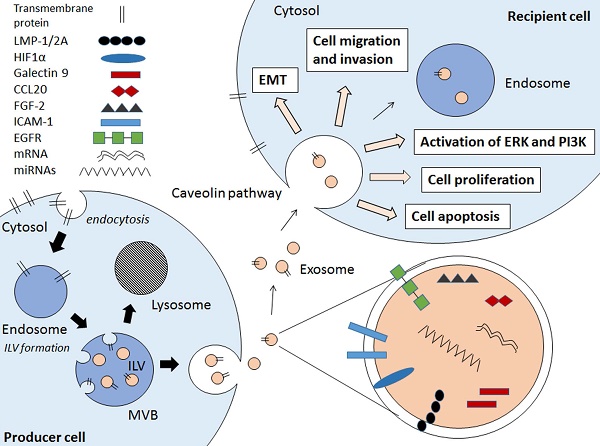
Exosomes are 40- to 100-nm membrane-bound small vesicles that carry a great variety of cellular cargoes including proteins, DNA, messenger RNAs (mRNAs), and microRNAs (miRNAs). These nanovesicles are detected in various biological fluids such as serum, urine, saliva, and seminal fluids. Exosomes serve as key mediators in intercellular communication by facilitating the transfer and exchange of cellular components from cells to cells. They contain various pathogenic factors whereby their adverse effects have been implicated in multiple viral infections and cancers. Interestingly, accumulating evidences showed that exosomes derived from tumour viruses or oncoviruses, exacerbate virus-associated cancers by remodelling the tumour microenvironment. In this review, we summarize the contributing factors of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) products-containing exosomes in viral pathogenesis and their potential implications in EBV-driven malignancies. Understanding the biological role of these exosomes in the disease would undoubtedly boost the development of a more comprehensive strategy to combat EBV-associated cancers and to better predict the therapeutic outcomes. Furthermore, we also highlight the potentials and challenges of EBV products-containing exosomes being employed as diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets for EBV-related cancers. Since these aspects are rather underexplored, we attempt to underline interesting areas that warrant further investigations in the future.
Keywords: Exosome, Epstein-Barr virus, EBV-associated cancer, LMP, nasopharyngeal carcinoma

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact