10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(10):1329-1340. doi:10.7150/ijbs.19752 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Erythropoietin Reduces Insulin Resistance via Regulation of Its Receptor-Mediated Signaling Pathways in db/db Mice Skeletal Muscle
1. Division of Nephrology, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China;
2. Division of Nephrology, Shanghai Pudong Hospital, Fudan University Pudong Medical Center, Shanghai, China;
3. Hemodialysis Center, Baoshan Branch of Shanghai No.1 People's Hospital, Shanghai, China.
Abstract
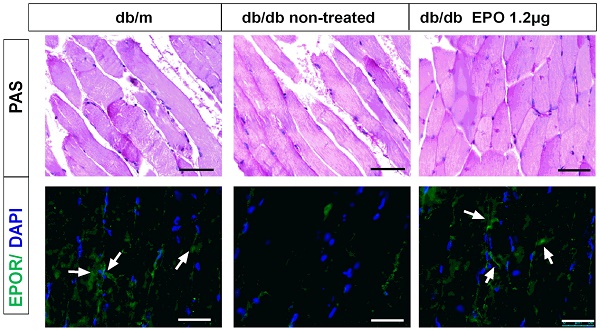
Erythropoietin (EPO) can reduce insulin resistance (IR) in adipocytes; however, it is unknown whether EPO can decrease IR in skeletal muscle. Here we investigated whether EPO could reduce IR in type 2 diabetic mouse skeletal muscle and its possible signaling mechanisms of action. Twelve-week-old db/db diabetic mice were employed in this study. Systemic use of EPO improved glucose profiles in type 2 diabetic mice after 4 and 8 weeks treatment. EPO up-regulated EPOR protein expression in skeletal muscle, and subsequently activated downstream signaling molecules such as JAK2, IRS-1, PI3K, AKT, and eNOS. We next constructed lentivirally-delivered shRNAs against EPOR and transfected skeletal muscle cells to knockdown EPOR. EPOR knockdown inhibited EPO induced JAK2, IRS-1, PI3K, AKT, eNOS signaling transduction, autophagy and Glut 4 translocation, as well as promoted apoptosis in skeletal muscle. Thus, EPO reduces skeletal muscle IR in type 2 diabetic mice via its specific receptor, EPOR. Possible mechanisms involved in its action may include increased autophagy and reduced apoptosis in type 2 diabetic skeletal muscles, which provides a new strategy for the treatment of IR.
Keywords: Erythropoietin (EPO), Erythropoietin receptor EPOR, Insulin resistance (IR), Skeletal muscle, type 2 diabetes, Insulin signaling.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact