10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2017; 13(11):1398-1408. doi:10.7150/ijbs.22249 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Targeting the long noncoding RNA MALAT1 blocks the pro-angiogenic effects of osteosarcoma and suppresses tumour growth
1. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People's Hospital, 600 Yishan Road, Shanghai 200233, China;
2. Department of Nursing, Guangming Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Pudong New Area, Shanghai 201300, China.
* Co-first authors: These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
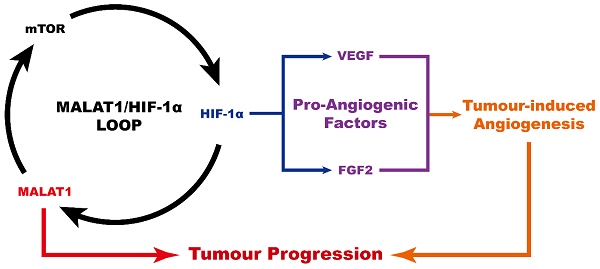
Osteosarcoma (OS), the commonest primary malignant tumour originating from bone, affects a substantial number of people, mostly during adolescent growth, and leads to a very poor prognosis as a result of the high rate of early metastases. Consequently, there is urgent demand for a novel treatment for this disease. There are growing concerns focused on OS-induced pro-angiogenic effects, but to date, the mechanism of OS-induced pro-angiogenesis is still insufficiently well-understood. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have attracted increasing interest due to their strong correlation with a variety of diseases and their powerful capacity for epigenetic regulation. Recently, metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1), a lncRNA, has been discovered to be closely related to OS progression and hypoxia responses which are associated with angiogenesis. In this study, we confirm that MALAT1 induces pro-angiogenic effects, and demonstrate that the underlying mechanism involves a MALAT1/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR)/hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) loop. With the help of chemically-modified small interfering RNAs targeting MALAT1 (siMALAT1), we confirm that siMALAT could provide a potential strategy to block the abnormally active OS-induced pro-angiogenic effect, and ultimately successfully suppress progression of OS tumours.
Keywords: osteosarcoma, MALAT1, siRNA, angiogenesis, oncotherapy.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact