10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(1):100-110. doi:10.7150/ijbs.22555 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MiR-21-mediated Metabolic Alteration of Cancer-associated Fibroblasts and Its Effect on Pancreatic Cancer Cell Behavior
1. Department of General Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Medical College, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, Shaanxi 710004 China;
2. Department of Pathology, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai 200032 China;
3. Graduate School, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an 710033, China.
4. Department of Surgical Oncology, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas, United States of America.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
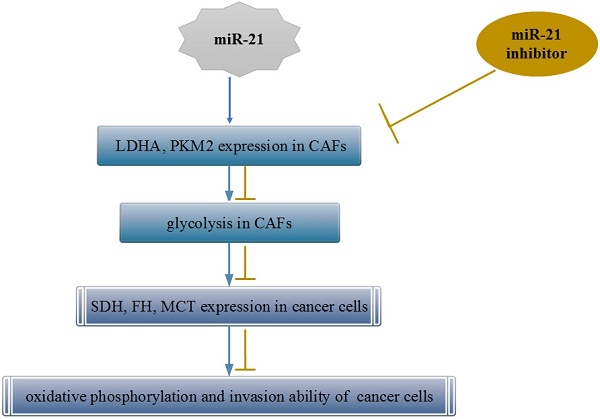
In this study, we investigated whether the metabolic alteration of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) occurs via miR-21 remodeling and the effect of this alteration on pancreatic cancer cells. CAFs and normal fibroblasts (NFs) were isolated and cultured. Glucose consumption and lactic acid production were tested, and lactate dehydrogenase (LDHA), pyruvate kinase m2 (PKM2), and miR-21 expression were examined. The level of glycolysis in CAFs was determined after treatment with a miR-21 inhibitor. Primary miR-21-NC CAFs and miR-21-inhibitor CAFs were indirectly co-cultured with BxPc-3 in vitro, and the invasion capacity of these cells was determined. The aerobic oxidation index of cancer cells and the expression of succinodehydrogenase (SDH) and fumarate hydratase (FH) were assessed. Compared with NFs, CAFs showed enhanced glucose uptake capacity, lactic acid production, and elevated LDHA, PKM2, and miR-21 expression. After miR-21 inhibitor treatment, the extent of glycolysis in CAFs was reduced. After indirect co-culture with CAFs, oxidative phosphorylation and SDH, FH, and MCT expression increased in BxPc-3 cells. After co-culture with miR-21-inhibitor-CAFs, oxidative phosphorylation and invasion ability of the pancreatic cancer cells decreased. MiR-21 was involved in metabolic alteration of CAFs and affected the development of cancer cells. This metabolic alteration may be an important mechanism by which the microenvironment promotes tumor progression in a nonvascular manner.
Keywords: miR-21, cancer-associated fibroblasts, glycolysis, metabolic alteration

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact