10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(5):508-517. doi:10.7150/ijbs.23318 This issue Cite
Research Paper
DNA damage checkpoint pathway modulates the regulation of skeletal growth and osteoblastic bone formation by parathyroid hormone-related peptide
1. State Key Laboratory of Reproductive Medicine, The Research Center for Bone and Stem Cells, Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China;
2. Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology, Suzhou Vocational Health College, Suzhou, China;
3. Department of Medicine, McGill University, Canada;
4. The Research Center for Aging Research, Friendship Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University Plastic Surgery, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
Abstract
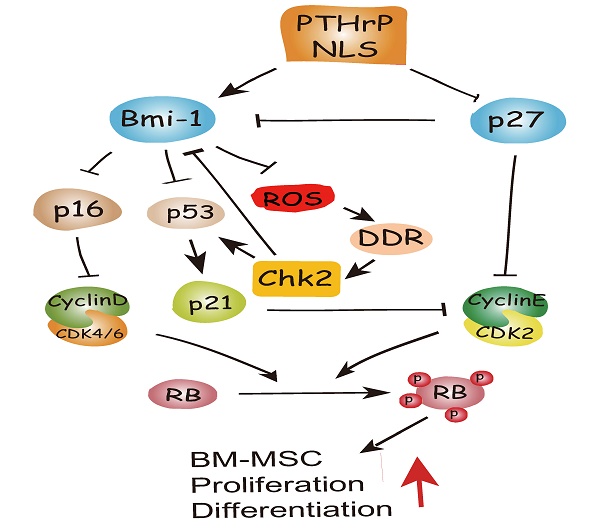
We previously demonstrated that parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP) 1-84 knockin (Pthrp KI) mice, which lacked a PTHrP nuclear localization sequence (NLS) and C-terminus, displayed early senescence, defective osteoblastic bone formation, and skeletal growth retardation. However, the mechanism of action of the PTHrP NLS and C-terminus in regulating development of skeleton is still unclear. In this study, we examined alterations of oxidative stress and DNA damage response-related molecules in Pthrp KI skeletal tissue. We found that ROS levels, protein expression levels of γ-H2AX, a DNA damage marker, and the DNA damage response markers p-Chk2 and p53 were up-regulated, whereas gene expression levels of anti-oxidative enzymes were down-regulated significantly. We therefore further disrupted the DNA damage response pathway by deleting the Chk2 in Pthrp KI (Chk2-/-KI) mice and did comparison with WT, Chk2-/- and Pthrp KI littermates. The Pthrp KI mice with Chk2 deletion exhibited a longer lifespan, improvement in osteoblastic bone formation and skeletal growth including width of growth plates and length of long bones, trabecular and epiphyseal bone volume, BMD, osteoblast numbers, type I collagen and ALP positive bone areas, the numbers of total colony-forming unit fibroblasts (CFU-f), ALP+ CFU-f and the expression levels of osteogenic genes. In addition, the genes associated with anti-oxidative enzymes were up-regulated significantly, whereas the tumor suppressor genes related to senescence were down-regulated in Chk2-/- KI mice compared to Pthrp KI mice. Our results suggest that Chk2 deletion in Pthrp KI mice can somewhat rescue defects in osteoblastic bone formation and skeletal growth by enhancing endochondral bone formation and osteogenesis. These studies therefore indicate that the DNA damage checkpoint pathway may be a target for the nuclear action of PTHrP to regulate skeletal development and growth.
Keywords: PTHrP, Chk2, osteoblastic bone formation, skeletal growth

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact