10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(10):1175-1185. doi:10.7150/ijbs.26011 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Astemizole Inhibits mTOR Signaling and Angiogenesis by Blocking Cholesterol Trafficking
1. Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Macau, Taipa, Macau SAR, China
2. Department of Pharmacology and Molecular Sciences, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA; The SJ Yan and HJ Mao Laboratory of Chemical Biology, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA
3. Key Laboratory of Metabolism and Molecular Medicine, Ministry of Education, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China
4. Chemical Genomics Global Research Laboratory, Department of Biotechnology, College of Life Science & Biotechnology, Yonsei University, Seoul 120-749, Republic of Korea
5. Department of Oncology, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA
Abstract
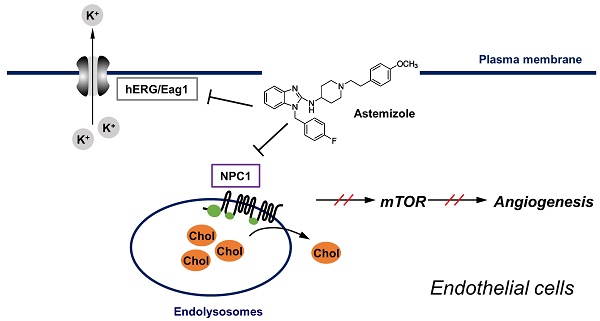
Cholesterol plays a key role in membrane protein function and signaling in endothelial cells. Thus, disturbing cholesterol trafficking is an effective approach for inhibiting angiogenesis. We recently identified astemizole (AST), an antihistamine drug, as a cholesterol trafficking inhibitor from a phenotypic screen. In this study, we found that AST induced cholesterol accumulation in the lysosome by binding to the sterol-sensing domain of Niemann-Pick disease, type C1 (NPC1), a lysosomal surface protein responsible for cholesterol transport. Inhibition of cholesterol trafficking by AST led to the depletion of membrane cholesterol, causing SREBP1 nuclear localization. The depletion of membrane cholesterol resulted in dissociation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) from the lysosomal surface and inactivation of mTOR signaling. These effects were effectively rescued by addition of exogenous cholesterol. AST inhibited endothelial cell proliferation, migration and tube formation in a cholesterol-dependent manner. Furthermore, AST inhibited zebrafish angiogenesis in a cholesterol-dependent manner. Together, our data suggest that AST is a new class of NPC1 antagonist that inhibits cholesterol trafficking in endothelial cells and angiogenesis.
Keywords: cholesterol trafficking, angiogenesis, astemizole, NPC1, mTOR

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact