10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(11):1483-1496. doi:10.7150/ijbs.27173 This issue Cite
Review
The PI3K/AKT pathway in obesity and type 2 diabetes
1. Guangdong Engineering Research Center of Natural Products and New Drugs, Guangdong Provincial University Engineering Technology Research Center of Natural Products and Drugs, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou (510006), China.
2. Guangdong Metabolic Diseases Research Center of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou (510006), China
3. Shenzhen Center for Disease Control and Prevention, 8 Longyuan Road, Nanshan District, Shenzhen (518055), China.
Abstract
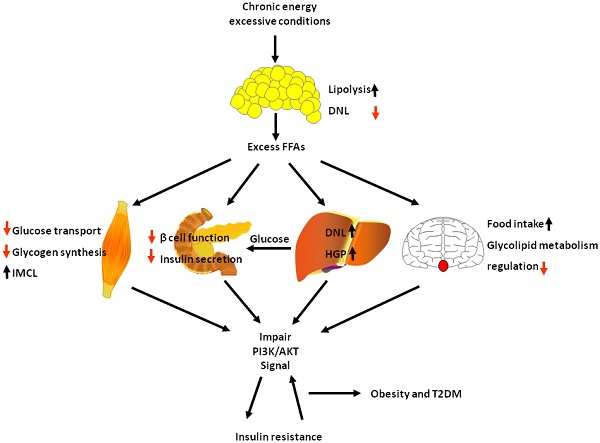
Obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus are complicated metabolic diseases that affect multiple organs and are characterized by hyperglycaemia. Currently, stable and effective treatments for obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus are not available. Therefore, the mechanisms leading to obesity and diabetes and more effective ways to treat obesity and diabetes should be identified. Based on accumulated evidences, the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway is required for normal metabolism due to its characteristics, and its imbalance leads to the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. This review focuses on the role of PI3K/AKT signalling in the skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, liver, brain and pancreas, and discusses how this signalling pathway affects the development of the aforementioned diseases. We also summarize evidences for recently identified therapeutic targets of the PI3K/AKT pathway as treatments for obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. PI3K/AKT pathway damaged in various tissues of the body leads to obesity and type 2 diabetes as the result of insulin resistance, and in turn, insulin resistance exacerbates the PI3K/AKT pathway, forming a vicious circle.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact