10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(13):1901-1909. doi:10.7150/ijbs.25306 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Generation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Human Embryonic Stem Cells in a Complete Serum-free Condition
Centre of Reproduction, Development & Aging, and Institute of Translational Medicine, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Macau, Taipa, Macau, China
*These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
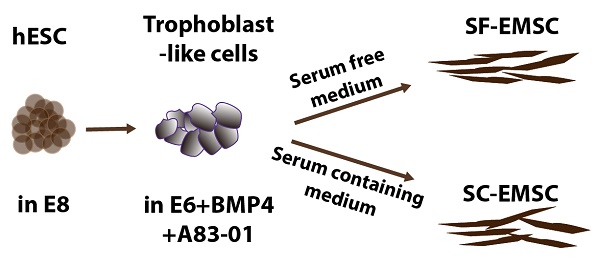
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) have been derived from a variety of tissues, and cultured either in animal serum-containing (SC) or serum-free (SF) media. We have previously derived MSC from human embryonic stem cells via an intermediate trophoblast step (named EMSC), which also have immunosuppressive and therapeutic effects on animal models of autoimmune disease. To promote the clinical application of this new source of MSC, we report here EMSC derived and cultured in a SF medium MesenCult (SF-EMSC) in comparison with a SC medium (SC-EMSC). SF-EMSC derived in MesenCult also expressed typical MSC markers CD73, CD90, and CD105, and manifested multipotency to differentiate to osteocytes, chondrocytes, and adipocytes. Comparably, CD105+ cells reached 90% about one week slower in the SF than SC conditions, and the proliferation rate was slightly faster for SF-EMSC than SC-EMSC at later passages. Both SF- and SC-EMSC responded similarly to the inflammatory stimulus IFNγ. However, the inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IL-8 were expressed much less in SF-EMSC than SC-EMSC. Furthermore, knockdown of P16INK4A in both SF- and SC-EMSC reduced replicative senescence. Together, our results suggest that EMSC can be generated in a complete SF condition, and SF-EMSC are largely similar to SC-EMSC. However, it takes longer time to derive EMSC in the SF than SC conditions, and the SF-EMSC proliferate faster at later passages and produce less of the inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IL-8 than SC-EMSC. This study provides important information for production of clinically applicable EMSC.
Keywords: Serum, mesenchymal stem cells, human embryonic stem cells, derivation, and culture

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact