10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(2):265-276. doi:10.7150/ijbs.30121 This issue Cite
Review
Role of Nutrition in the Pathogenesis and Prevention of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Recent Updates
1. Department of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310051, China
2. Department of Neurobiology, Institute of Neuroscience, and the Collaborative Innovation Center for Brain Science, Key Laboratory of Medical Neurobiology of the Ministry of Health of China, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310058, China
3. Institute of Hydrobiology, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, 430072, China
4. Laboratory of Reproductive Neuroendocrinology, Department of Animal Sciences, Faculty of Biological Sciences, Quaid-i-Azam University, Islamabad, Pakistan
Abstract
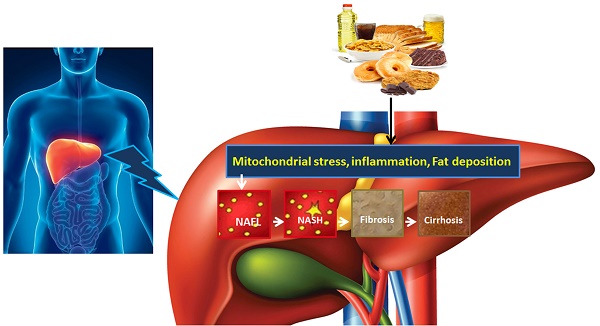
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is an acquired metabolic disease characterized by triglycerides (TGs) deposition in liver induced by other factors rather than alcohol consumption. NAFLD significantly contributes to liver diseases in children and adults. NAFLD pathogenesis is associated with age, gender, race and ethnicity. Insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, elevated plasma free fatty acids (FFAs), fatty liver, hepatocyte injury, liver inflammation, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, imbalanced pro-inflammatory cytokines, and fibrosis are the characteristics of NAFLD. Factors including genetic and epigenetic pathways, sedentary lifestyle, sleep, and diet composition affect NAFLD pathogenesis. In this review, we discuss the aetiology, risk factors and pathogenesis of NAFLD. Special focus is given to macro and micro nutrition as causing factors and their role in the prevention of NAFLD pathogenesis.
Keywords: nutrition, hepatic inflammation, NAFLD pathogenesis, prevention

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact