10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(2):298-311. doi:10.7150/ijbs.29183 This issue Cite
Review
Signaling Mechanisms Underlying Genetic Pathophysiology of Craniosynostosis
1. Department of Orthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, No. 22 Zhongguancun Avenue South, Haidian District, Beijing, 100081, PR. China
2. National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology,Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, No. 22 Zhongguancun Avenue South, Haidian District, Beijing, 100081, PR. China
Abstract
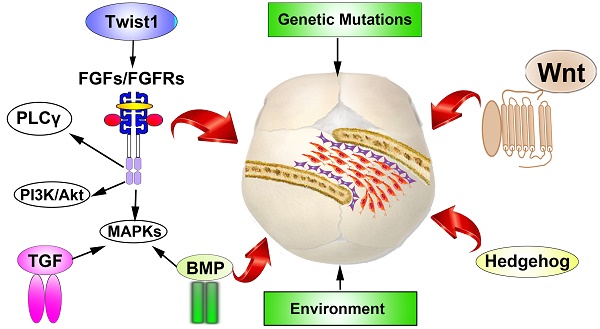
Craniosynostosis, is the premature fusion of one or more cranial sutures which is the second most common cranial facial anomalies. The premature cranial sutures leads to deformity of skull shape and restricts the growth of brain, which might elicit severe neurologic damage. Craniosynostosis exhibit close correlations with a varieties of syndromes. During the past two decades, as the appliance of high throughput DNA sequencing techniques, steady progresses has been made in identifying gene mutations in both syndromic and nonsyndromic cases, which allow researchers to better understanding the genetic roles in the development of cranial vault. As the enrichment of known mutations involved in the pathogenic of premature sutures fusion, multiple signaling pathways have been investigated to dissect the underlying mechanisms beneath the disease. In addition to genetic etiology, environment factors, especially mechanics, have also been proposed to have vital roles during the pathophysiological of craniosynostosis. However, the influence of mechanics factors in the cranial development remains largely unknown. In this review, we present a brief overview of the updated genetic mutations and environmental factors identified in both syndromic and nonsyndromic craniosynostosis. Furthermore, potential molecular signaling pathways and its relations have been described.
Keywords: Craniosynostosis, Signaling Pathways, Genetic Mutations.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact