10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(2):441-452. doi:10.7150/ijbs.26826 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Hypoxia-elevated circELP3 contributes to bladder cancer progression and cisplatin resistance
1. The Department of Urology, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China;
2. The Department of Urology, Yan'an Hospital Affiliated with Kunming Medical University, Kunming, China;
3. The Department of Pediatric Surgery, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China;
4. The Department of Urology, Zhujiang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
*Authors who contributed equally to this article.
Abstract
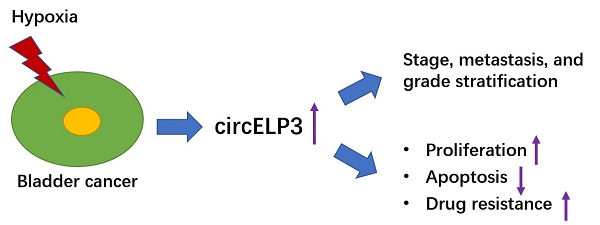
Hypoxia plays a critical role in cancer biology. It induces genomic instability, which in turn helps cancer cells respond adaptively to meet the needs of carcinogenesis, cancer progression and relapse. Circular RNA has not been reported among the variety of downstream factors in this adaptive response. Although a few studies have demonstrated the important role of circular RNAs in driving human bladder cancer progression, their carcinogenic roles are still under investigated. Here, we identified a hypoxia-elevated circular RNA, circELP3, that contributes to bladder cancer progression and cisplatin resistance. Decreasing the level of circELP3 via siRNA clearly reduced the in vitro proliferation and cisplatin resistance of bladder cancer cells and promoted apoptosis. Interfering with circELP3 suppressed tumor xenograft growth in nude mice in vivo. In addition, lower circELP3-expressing bladder cancer cells displayed poorer self-renewal capacity, as demonstrated by lower levels of sphere formation and stem cell marker expression. Furthermore, in human bladder cancer patients, strong correlations between a high circELP3 level and advanced tumor grade and lymph node metastasis were observed. In summary, we provide the first direct evidence that circular RNA participates in the adaptive response to hypoxia and may play a role in the progression and drug resistance of bladder cancer.
Keywords: Hypoxia, Circular RNA, Bladder cancer, Progression, Cisplatin resistance

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact