10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(5):999-1009. doi:10.7150/ijbs.29805 This issue Cite
Research Paper
FePt/GO Nanosheets Suppress Proliferation, Enhance Radiosensitization and Induce Autophagy of Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells
1. Department of Radiation and Medical Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
2. Key Laboratory of Artificial Micro- and Nano-Structures of Ministry of Education, School of Physics and Technology, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
3. Department of Biological Repositories, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
4. Department of Urology, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
5. Hubei Key Laboratory of Tumour Biological Behaviors, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
6. Hubei Cancer Clinical Study Center, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
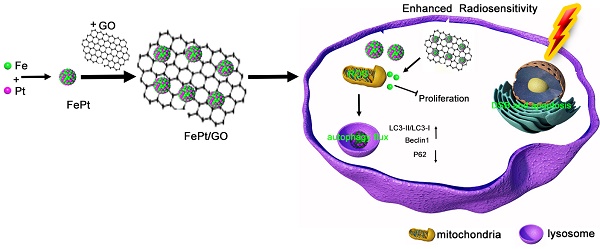
With the advancement of nanotechnology, various nanocomposites have been applied in the diagnostics and treatment of cancer. We synthetized FePt nanoparticles which were assembled on the surface of graphene oxide (GO). These novel FePt/GO nanosheets simultaneously act as a chemotherapy drug and enhance radiosensitivity. In this study, transmission electron microscope, dynamic light scattering, X-ray photoelectron spectroscope and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy were used to characterize surface morphology and chemical composition of FePt/GO nanosheets (NSs). Their cytotoxicity in various cancer and normal cells was evaluated by cell counting kit-8 assay, and their effects on radiosensitization were determined by colony formation assay. To explore the underlying mechanisms, we measured the intracellular reactive oxygen species levels and autophagy formation. Monodansylcadaverine-staining, Western Blotting and ultrastructure analysis were utilized to assess autophagy. The results demonstrated that FePt/GO NSs not only selectively suppressed the proliferation of cancer cells, but also increased their radiosensitization. Moreover, FePt/GO NSs induced autophagy, which might result in promoted sensibilization of radiotherapy. In conclusion, with good safety and efficacy, FePt/GO NSs are safe and effective to suppress proliferation, enhance radiosensitization and induce autophagy of human non-small cell lung cancer cells. They are potential for the treatment of lung cancer.
Keywords: FePt/GO nanosheets, radiosensitization, lung cancer, autophagy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact