10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(5):1052-1071. doi:10.7150/ijbs.31143 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Construing the Biochemical and Molecular Mechanism Underlying the In Vivo and In Vitro Chemotherapeutic Efficacy of Ruthenium-Baicalein Complex in Colon Cancer
1. Department of Nephrology, China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin, 130033, China
2. Department of Radiotherapy, The Second Hospital of Jilin university, Changchun, Jilin, 130041, China
3. Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, NSHM Knowledge Campus- Kolkata, 124 B.L. Saha Road, Kolkata -700053, West Bengal, India
Abstract
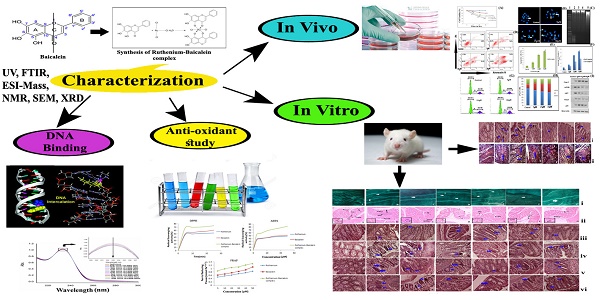
In pursuit of a novel approach in colon cancer therapy, we explored the ability of ruthenium baicalein complex to eradicate colon cancer by efficiently targeting various apoptotic pathways on human colon cancer cell line and on a DMH and DSS induced murine model of colorectal cancer. In this study, we provide direct proof of the chemotherapeutic potential of the ruthenium baicalein complex by activating p-53 dependent intrinsic apoptosis and modulating the AKT/mTOR and WNT/β- catenin pathways. The ruthenium baicalein complex was synthesized and its characterizations were accomplished through various spectroscopic techniques followed by assessment of antioxidant potential by DPPH, FRAP, and ABTS methods. In vitro study established that the complex increased p53 and caspase-3 expressions while down regulating VEGF and mTOR expression, induced apoptosis, and DNA fragmentation in the HT-29 cells. Acute and sub-acute toxicity study was also considered and results from in vivo study revealed that complex was effective in suppressing ACF multiplicity and hyperplastic lesions and also raised the CAT, SOD, and glutathione levels. Furthermore, the complex decreased cell proliferation and increased apoptotic events in tumor cells correlated with the upregulation of Bax and downregulation of Bcl2, WNT and β- catenin expressions. Our findings from the in vitro and in vivo study provide robust confirmation that ruthenium baicalein complex possesses a potential chemotherapeutic activity against colon cancer and is competent in reducing ACF multiplicity, hyperplastic lesions in the colon tissues of rats by inducing apoptosis.
Keywords: ruthenium baicalein complex, structural characterization, in vitro study, toxicity study, colon carcinogenesis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact