10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(6):1310-1324. doi:10.7150/ijbs.32987 This issue Cite
Research Paper
CSN6 Promotes the Migration and Invasion of Cervical Cancer Cells by Inhibiting Autophagic Degradation of Cathepsin L
1. Laboratory of Clinical and Experimental Pathology, Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221004, Jiangsu, China
2. Department of Rehabilitation, The Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221002, China
*These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
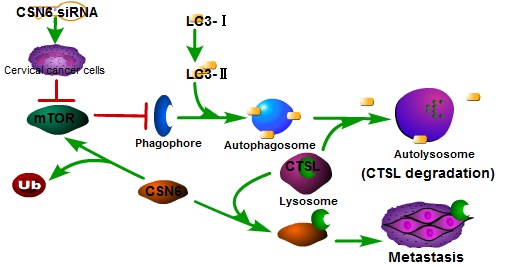
CSN6 is one subunit of the highly conserved constitutive photomorphogenesis 9 (COP9) signalosome (CSN), which is overexpressed in many types of cancers, and has received great attention as a regulator of the degradation of cancer-related proteins, suggesting its importance in oncogenic activity. CSN6 has been shown to be overexpressed in cervical cancer (CC) and associated with CC development. CC remains to be one of the most aggressive cancers affecting women. Cathepsin L (CTSL), significantly associated with the autophagy, plays a critical role in degradation of extracellular matrix for metastasis. However, the detailed biological functions of CSN6 on CTSL in CC metastasis have not been well clarified. Our data has shown that CSN6 and CTSL are positively correlated. The overexpression of CSN6 and CTSL might be a strong indicator for CC enhanced aggressiveness. CSN6 could suppress the degradation of CTSL, then facilitated the migration and invasion of CC cells. Interestingly, our results indicated that autophagy is essential for decreasing CTSL, while CSN6 could inhibit the autophagy ability of CC cells. In addition, blocking of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway reversed CSN6-mediated autophagy inhibition. We further demonstrated that CSN6 positively regulated CTSL expression through an autophagy-lysosomal system. Taken together, we concluded that CSN6 might promote the migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells by inhibiting autophagic degradation of CTSL and serve as a potential gene therapy target for the treatment of CC metastasis.
Keywords: CSN6, autophagy, CTSL, metastasis, cervical cancer

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact