10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(8):1654-1663. doi:10.7150/ijbs.33837 This issue Cite
Review
Treatment implications of natural compounds targeting lipid metabolism in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity and cancer
1. Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Invasion, Chinese Ministry of Education, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410078, PR China.
2. Cancer Research Institute and School of Basic Medical Science, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410078, PR China.
3. Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis, Chinese Ministry of Health, Changsha, Hunan 410078,PR China.
4. Department of Respiratory Medicine, Shenzhen Longgang Center Hospital, Shenzhen, Guangdong 518116, PR China.
5. Department of Ultrasound Imaging,Xiangya Hospital,Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410078, PR China.
6. Department of Medicine, Hunan Traditional Chinese Medical College, Zhuzhou, Hunan 412000, China.
7. The Hormel Institute, University of Minnesota, Austin, MN 55912, USA.
8. Molecular Imaging Research Center of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410078, China.
* These authors contribute equally to the paper
Abstract
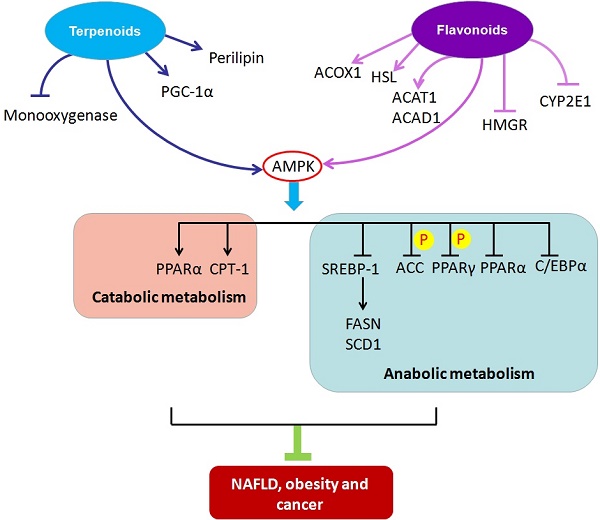
Metabolic disorders can lead to a scarcity or excess of certain metabolites such as glucose, lipids, proteins, purines, and metal ions, which provide the biochemical foundation and directly contribute to the etiology of metabolic diseases. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity, and cancer are common metabolic disorders closely associated with abnormal lipid metabolism. In this review, we first describe the regulatory machinery of lipid metabolism and its deregulation in metabolic diseases. Next, we enumerate and integrate the mechanism of action of some natural compounds, including terpenoids and flavonoids, to ameliorate the development of metabolic diseases by targeting lipid metabolism. Medicinal natural products have an established history of use in health care and therapy. Natural compounds might provide a good source of potential therapeutic agents for treating or preventing metabolic diseases with lipid metabolic abnormalities.
Keywords: natural compound, lipid metabolism, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity, cancer

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact