10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(11):2308-2319. doi:10.7150/ijbs.33432 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MicroRNA-106a Provides Negative Feedback Regulation in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation by targeting TLR4
Department of Clinical Veterinary Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430070, People's Republic of China. College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, 430070, People's Republic of China.
Abstract
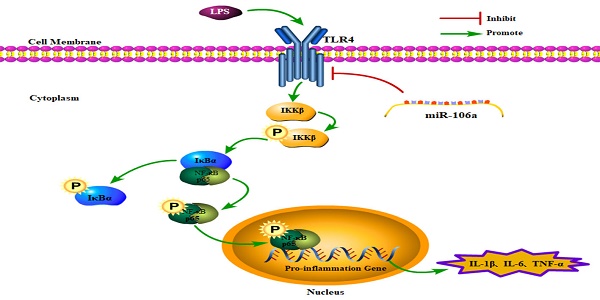
Acute lung injury (ALI) is a common clinical disease with high incidence and mortality rate, which is characterized by severe inflammatory response and tissues damage. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been regarded as novel regulators of inflammation, and play an important role in various inflammatory diseases. However, it remains unknown whether the regulatory mechanisms mediated by miR-106a is involved in LPS-induced ALI. In this study, we found that expression of miR-106a was significantly decreased in lung tissues of ALI mice and LPS-stimulated macrophages. We also revealed that over-expression of miR-106a significantly decreased the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α, whereas this effect was reversed by the inhibition of miR-106a. Moreover, miR-106a inhibits NF-κB activation by targeting TLR4 expression. We further demonstrated that miR-106a inhibited TLR4 expression via binding directly to the 3'-UTR of TLR4. Taken together, the results of the present study illuminated that miR-106a is a negative feedback regulator in LPS-stimulated inflammation through TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.
Keywords: ALI, miR-106a, NF-κB, TLR4

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact