10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(11):2497-2508. doi:10.7150/ijbs.37481 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Xanthohumol inhibits colorectal cancer cells via downregulation of Hexokinases II-mediated glycolysis
1. Department of Pathology, Hunan Cancer Hospital and The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410006, P.R. China
2. Department of Radiology, The Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410013, P.R. China
3. Clinical Center for Gene Diagnosis and Therapy, The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410011, P.R. China
4. Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410011, P.R. China
5. Department of Cancer Biology, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic, 9500 Euclid Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44195, USA
Abstract
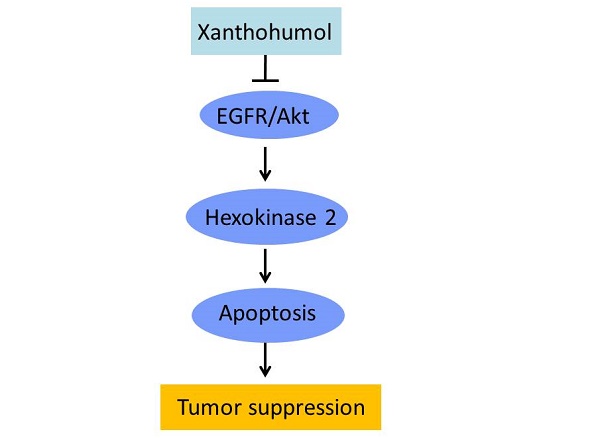
Deregulation of glycolysis is a common phenomenon in human colorectal cancer (CRC). In the present study, we reported that Hexokinase 2 (HK2) is overexpressed in human CRC tissues and cell lines, knockout of HK2 inhibited cell proliferation, colony formation, and xenograft tumor growth. We demonstrated that the natural compound, xanthohumol, has a profound anti-tumor effect on CRC via down-regulation of HK2 and glycolysis. Xanthohumol suppressed CRC cell growth both in vitro and in vivo. Treatment with xanthohumol promoted the release of cytochrome C and activated the intrinsic apoptosis pathway. Moreover, our results revealed that xanthohumol down-regulated the EGFR-Akt signaling, exogenous overexpression of constitutively activated Akt1 significantly impaired xanthohumol-induced glycolysis suppression and apoptosis induction. Our results suggest that targeting HK2 appears to be a new approach for clinical CRC prevention or treatment.
Keywords: Xanthohumol, HK2, glycolysis, Akt, colorectal cancer

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact