10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(13):2798-2814. doi:10.7150/ijbs.33779 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Disrupted balance of CD4+ T-cell subsets in bone marrow of patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia
1. Department of Hematology, Qilu Hospital, Shandong University, 107 West Wenhua Road, Jinan, P. R. China;
2. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Qilu Hospital, Shandong University (Qingdao), 758 Hefei Road, Qingdao, P. R. China;
3. School of Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Qilu University of Technology, 3501 Daxue Road, Jinan, P. R. China;
4. Department of Radiotherapy, Zhangqiu People's Hospital, 1920 Huiquan Road, Jinan, P. R. China;
5. Department of Hematology, Taian Central Hospital, Taian, P. R. China;
6. Department of Orthopedics, Shandong Provincial Qianfoshan Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan, China
7. Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Remodeling and Function Research, Chinese Ministry of Education and Chinese Ministry of Health, Jinan, China
Abstract
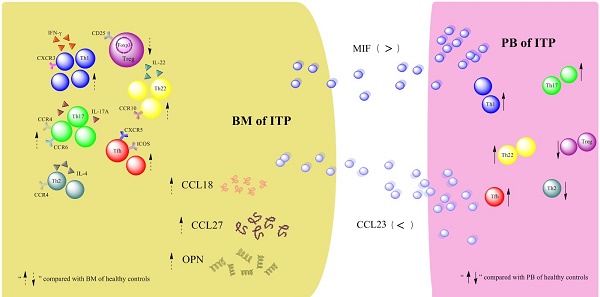
Disequilibrium of CD4+ T-cell subpopulations in peripheral blood (PB) of patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) has been well established, whereas the profile of CD4+ T-cell subpopulations in bone marrow (BM) remains elusive. In the present study, the frequencies of T helper 22 (Th22), Th17, Th1, Th2, follicular T helper (Tfh) cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs) as well as their effector cytokines in BM and PB from active ITP patients and healthy controls (HCs) were determined. Results showed that the frequencies of Th22, Th17, Th1, and Tfh cells were significantly higher, but Treg number was remarkably lower in BM from ITP patients than from HCs. In the ITP group, it was notable that the numbers of BM Th22, Th17, Th1, Th2, and Tfh cells were significantly elevated compared with the matched PB counterparts, while Treg number in BM was considerably reduced compared with that in PB. In consistence with the BM Th subset pattern, plasma levels of interleukin (IL)-22, IL-17A, and interferon (INF)-γ in BM from ITP patients were significantly increased compared with that from HCs. Therefore, the balance of CD4+ T-cell subsets was disrupted in both BM and PB of ITP patients, suggesting that this might play important roles in the pathophysiological process of ITP.
Keywords: Primary immune thrombocytopenia, T helper cells, regulatory T cells, bone marrow

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact