10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(13):2936-2947. doi:10.7150/ijbs.38000 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MiR-4319 induced an inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and prevented cancer stemness of HCC through targeting FOXQ1
1. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, No. 277 Yanta West Road, Xi'an 710061, China
2. Department of oncology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, No. 277 Yanta West Road, Xi'an 710061, China
#Equate contributions
Abstract
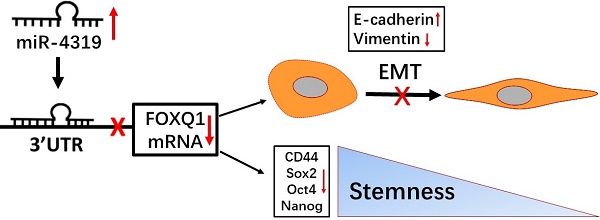
The heterogeneity existing in tumours is responsible for the poor response to treatment. Therefore, elucidating the molecular mechanisms of intratumoural heterogeneity in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is vital for the discovery of new therapeutic methods for improving the prognosis of patients. Of note, cancer stem cells (CSCs) existing in HCC may explain the pathological properties of heterogeneity and recurrence. An increasing number of studies have confirmed that abnormally expressed microRNAs (miRNAs) take part in the carcinogenesis as well as the aggravation of HCC. However, little information is currently available about the specific miR-4319 in HCC. Herein, we demonstrated that the level of miR-4319 was remarkably decreased in HCC specimens and cells compared to that in normal counterparts and that the depression of miR-4319 in tumour specimens correlates with tumour size, histological grade and venous invasion. Through a series of functional experiments, we illustrated that miR-4319 repressed cell proliferation, accelerated apoptosis, inhibited epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and prevented cancer stemness in HCC cells by targeting FOXQ1 (Forkhead box Q1). An in vivo tumourigenesis assay uncovered that depletion of miR-4319 in Hep3B cells increased tumour growth and elevated the expression of EMT and CSC markers in comparison to those of the control group. Restoration of FOXQ1 expression also partially reversed the miR-4319-induced biological effects on HCC cells. Thus, miR-4319, as a posttranscriptional regulator, plays a profound role in suppressing the malignant progression of HCC, and our study highlights the miR-4319/FOXQ1 cascade as a potential therapeutic target for conquering HCC.
Keywords: miR-4319, FOXQ1, EMT, cancer stemness, HC

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact