10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(1):147-161. doi:10.7150/ijbs.36955 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Shikonin induces colorectal carcinoma cells apoptosis and autophagy by targeting galectin-1/JNK signaling axis
1. State Key Laboratory of Southwestern Chinese Medicine Resources, School of Pharmacy, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 611137, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center, West China Hospital, and West China School of Pharmacy, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, China
*These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
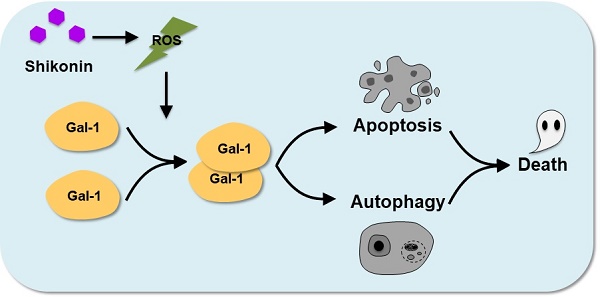
Colorectal carcinoma (CRC) is the third most common malignant tumor pathology worldwide. Despite progress in surgical procedures and therapy options, CRC is still a considerable cause of cancer-related mortality. In this study, we tested the antitumor effects of shikonin in CRC and tried to identify its potential mechanism. The potential target, molecular mechanism as well as in vitro and in vivo antitumor effects of shikonin in CRC cells were determined by an integrative protocol including quantitative proteomics, RT-PCR, western blotting, RNA interference and overexpression, apoptosis and autophagy assays, etc. Galectin-1 was a potential target of shikonin from the iTRAQ-based proteomic analysis in shikonin-treated SW620 cell. The overexpression and RNA silencing of galectin-1 in two CRC cells suggested that the shikonin sensitivity was correlation to galectin-1 levels. The ROS accumulation induced by shikonin was important to the formation of galectin-1 dimers. Dimer galectin-1 was found to be associated with the activation of JNK and downstream apoptosis or autophagy. Moreover, through functional in vitro studies, we showed that differences in galectin-1 level affected tumor cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. In summary, shikonin induced CRC cells apoptosis and autophagy by targeting galectin-1 and JNK signaling pathway both in vitro and in vivo, which suggested a potential novel therapy target for CRC.
Keywords: Shikonin, Colorectal carcinoma, Galectin-1, apoptosis, autophagy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact