10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(2):309-319. doi:10.7150/ijbs.37162 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Fangchinoline protects against bone loss in OVX mice via inhibiting osteoclast formation, bone resorption and RANKL-induced signaling
1. School of Biomedical Sciences, The University of Western Australia, Perth, Western Australia, 6009, Australia
2. Department of Endocrinology, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, 510700, China.
3. Orthopedic Department, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, China.
4. Department of Spine Surgery, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou Guangdong, 510630, P. R. China.
5. Research Centre for Regenerative Medicine and Guangxi Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Guangxi Medical University, Guangxi, 530021, China
*Authors equally contributed to this work.
Abstract
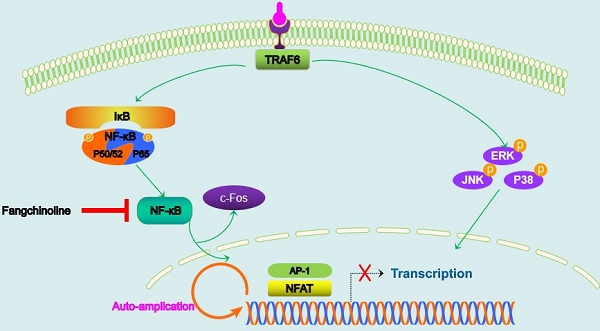
Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by abnormally increased formation and function of osteoclasts. Anti-RANKL treatment using natural medicine is a potential therapy for osteoporosis. Here, we studied the effect of fangchinoline, which is extracted from the root of Stephania tetrandra S. Moore, on osteoclast formation and function. We found that fangchinoline inhibited osteoclastogenesis at doses of 0.5 and 1 µM. In addition, we also examined the mechanism of the inhibitory effect of fangchinoline on osteoclasts. We found that fangchinoline down regulated NFATc1 activity and expression. However, fangchinoline did not affect IκBα degradation and MAPK pathways. In addition, we also found that fangchinoline could protect against bone loss in OVX mice. Taken together, fangchinoline may be a potential compound for osteoporosis.
Keywords: fangchinoline, RANKL, osteoclast, NF-κB, NFATc1, MAPK

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact