10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(2):353-364. doi:10.7150/ijbs.32331 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Attenuation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis
1. Department of Dermatology, Drug Hypersensitivity Clinical and Research Center, Chang Gung Memorial Hospitals, Linkou, Taipei, and Keelung, Taiwan.
2. Whole-Genome Research Core Laboratory of Human Diseases, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Keelung, Taiwan.
3. Chang Gung Immunology Consortium, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital and Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
4. College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
5. Graduate Institute of Clinical Medical Sciences, College of Medicine, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
6. Immune-Oncology Center of Excellence, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou, Taiwan.
7. Institute of Microbiology and Immunology, National Yang-Ming University, Taipei, Taiwan.
8. Department of Dermatology, Xiamen Chang Gung Hospitals, China.
Abstract
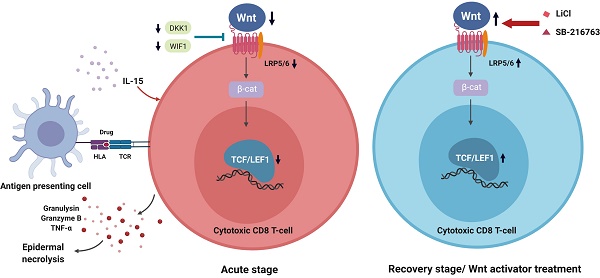
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrosis (TEN) are rare but life-threatening severe cutaneous adverse reactions. Current studies have suggested that the pathobiology of drug-mediated SJS/TEN involves a dysregulation of cellular immunity with overwhelming activation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. The canonical Wnt signaling pathway plays important roles in T cell development and activation, which may provide potential avenues for alleviating dysregulated immunity in SJS/TEN. In this study, we aimed to assess the implication of Wnt signaling in drug-reactive T cells in SJS/TEN. We showed downregulation of Wnt signaling components, including T cell factor 1 (TCF-1)/lymphoid enhancer binding factor 1 (LEF-1) transcription factors, in SJS/TEN patients, suggesting that canonical Wnt signaling is regulated during cytotoxic T cell responses in SJS/TEN. Further analyses demonstrated that engagement of the T cell receptor by antigen encounter and treatment of a prognostic marker of SJS/TEN, IL-15, in vitro led to the downregulation of LEF-1 and TCF-1 expression in CD8+ T cells. Enhancement of Wnt signaling by adding the Wnt activators attenuated ex vivo activation of drug-specific T cells from SJS/TEN patients, indicating a functional involvement of Wnt signaling in the pathomechanism of SJS/TEN. These findings provide additional insight into the immunopathogenesis and therapeutic intervention of this devastating condition.
Keywords: Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrosis (TEN), cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL), Wnt, T cell factor-1 (TCF-1), lymphoid enhancer binding factor 1 (LEF-1).

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact