10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(4):553-567. doi:10.7150/ijbs.40643 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The Role of Akt2 in the Protective Effect of Fenofibrate against Diabetic Nephropathy
1. Department of Nephrology, The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin, 130021, China;
2. Department of Gastrointestinal and Colorectal Surgery, China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin, 130033, China;
3. Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Changchun University of Chinese Medicine, Changchun, Jilin, 130117, China;
4. Pediatric Research Institute, Departments of Pediatrics, Radiation Oncology, Pharmacology and Toxicology, University of Louisville, Louisville, KY, 40202, USA.
*Y.C. and X.Z. contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
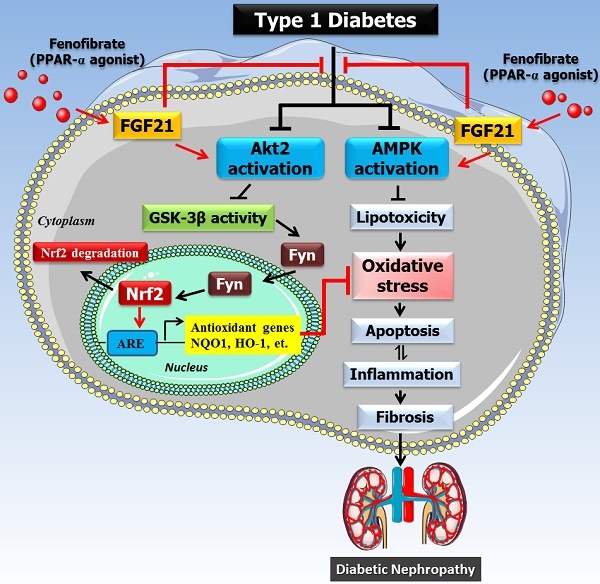
Fenofibrate (FF) protects against diabetic nephropathy (DN) in type 1 diabetic (T1D) mice by upregulating the expression of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), leading to the activation of the Akt-mediated Nrf2 antioxidant pathways. Here, we examined which isoforms of Akt contribute to FF activation of FGF21-mediated renal protection by examining the phosphorylation and expression of three isoforms, Akt1, Akt2, and Akt3. T1D induced by a single intraperitoneal dose of streptozotocin (STZ) resulted in reduced phosphorylation of one isoform, Akt2, but FF treatment increased renal Akt2 phosphorylation in these and normal mice, suggesting a potential and specific role for renal Akt2 in FF protection against T1D. This was further confirmed using in vitro cultured HK-2 human kidney tubule cells exposed to high glucose (HG) with siRNA silencing of the Akt2 gene and STZ-induced diabetic Akt2-knockout mice with and without 3-month FF treatment. In normal HK-2 cells exposed to HG for 24 hours, FF completely prevented cell death, reduced total Akt expression and glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3β phosphorylation, increased nuclear accumulation of Fyn, and reduced nuclear Nrf2 levels. These positive effects of FF were partially abolished by silencing Akt2 expression. Similarly, FF abolished T1D-induced renal oxidative stress, inflammation, and renal dysfunction in wild-type mice, but was only partially effective in Akt2-KO mice. Furthermore, FF treatment stimulated phosphorylation of AMPKα, an important lipid metabolism mediator, which in parallel with Akt2 plays an important role in FF protection against HG-induced HK-2 cells oxidative stress and damage. These results suggest that FF protects against DN through FGF21 to activate both Akt2/GSK-3β/Fyn/Nrf2 antioxidants and the AMPK pathway. Therefore, FF could be repurposed for the prevention of DN in T1D patients.
Keywords: diabetic nephropathy, Akt2, fibroblast growth factor 21, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α agonist.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact