10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(5):766-776. doi:10.7150/ijbs.40189 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Syndecan-4 is a Novel Therapeutic Target for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration via Suppressing JNK/p53 Pathway
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu 215006, China
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
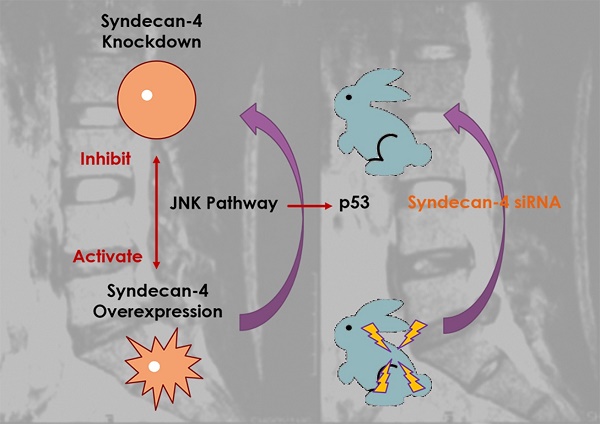
Syndecan-4 is a member of the polysaccharide syndecan family and plays a vital role in intervertebral disc development. Several studies have demonstrated the positive relationship between syndecan-4 expression and intervertebral disc degeneration. However, the detailed molecular mechanism by which syndecan-4 affects the degeneration of nucleus pulposus cells (NPCs) remains unclear. In this study, cell viability was determined by CCK-8 assay, mRNA level was determined by qPCR, and protein expression was determined by western blot. Molecular interaction was determined by chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. A rabbit intervertebral disc degeneration model was established to test for syndecan in vivo. We found that the morphology and viability of NPCs were not affected by the expression of syndecan-4 in the long term. While the NPC function were affected, which results in the degeneration of intervertebral disc. Syndecan-4 overexpression promoted the degeneration of NPCs. Syndecan-4 also activated the JNK signaling pathway and downstream p53 pathways, and promoted degeneration. Inhibition of the JNK pathway, which down-regulated p53 expression, alleviated the degeneration. In an in vivo study, syndecan-4 siRNA injection stopped the development of rabbit disc degeneration, and even created a reverse effect, in which JNK/p53 played a role. Syndecan-4 may be a novel therapeutic target for intervertebral disc degeneration via suppressing the JNK/p53 pathway.
Keywords: Syndecan-4, disc degeneration, JNK, p53, signal pathway

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact