10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(5):882-892. doi:10.7150/ijbs.40960 This issue Cite
Research Paper
IC261, a specific inhibitor of CK1δ/ε, promotes aerobic glycolysis through p53-dependent mechanisms in colon cancer
1. Department of Pathology, Xinxiang Medical University, Henan, China
2. Department of Pathology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinxiang Medical University, Henan, China
3. The Academic Affairs Office, Xinxiang Medical University, Henan, China
* contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
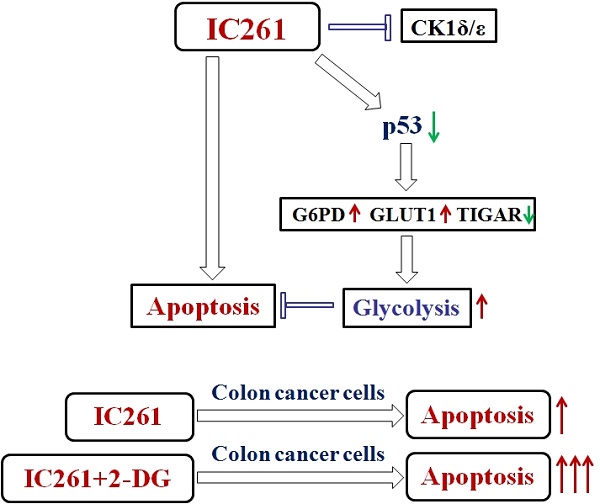
Casein kinase 1δ (CK1δ) and casein kinase 1ε (CK1ε) have been proposed to be involved in DNA replication, differentiation and apoptosis, thus participating in the regulation of tumorigenesis. However, their functions in colon cancer and the underlying mechanism remain unclear. Here, we found that the expression of CK1ε and CK1δ increased significantly in cancer tissues and the upregulation of CK1ε and CK1δ were closely related to poor differentiation, advanced TNM stage and poor prognosis of colon cancer. CK1δ/ε inhibitor IC261 could induce a decrease in cell survival and proliferation, and an increase in apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Interestingly, IC261 increased the level of aerobic glycolysis in colon cancer cells. Meanwhile, IC261 caused the decrease of p53 protein level and the misregulation of glycolysis related genes (TIGAR, G6PD, GLUT1) which are closely related to the regulation of glycolysis by p53. Inhibiting p53 by siRNA or inhibitor could significantly attenuate the upregulation of aerobic glycolysis induced by IC261. Finally, inhibition of aerobic glycolysis can further increase the cytotoxicity induced by IC261. Collectively, our results revealed that IC261 could inhibit the growth of colon cancer cells and increase the level of aerobic glycolysis, which is regulated by p53-dependent manner. This result suggested that targeting CK1δ/ε and glycolysis might be a valuable strategy treatment and combination therapies for colon cancer.
Keywords: colon cancer, casein kinase, aerobic glycolysis, IC261

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact