10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(8):1288-1301. doi:10.7150/ijbs.39098 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Selective targeting of the TLR4 co-receptor, MD2, prevents colon cancer growth and lung metastasis
1. Chemical Biology Research Center, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, 325035, P. R. China.
2. Department of Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, 325035, P. R. China.
*These authors contributed equally to this study.
Abstract
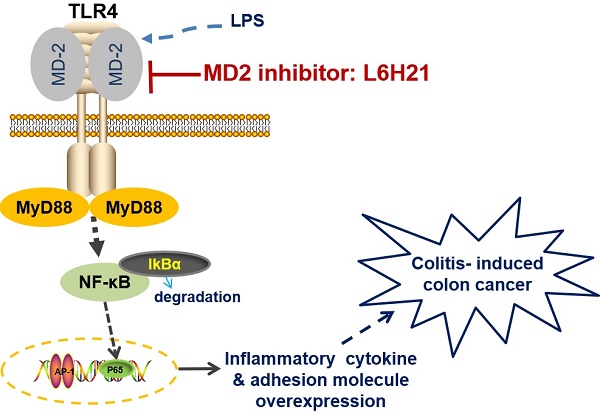
Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling is an emerging pathway in tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Myeloid differentiation protein-2 (MD2) contributes to ligand recognition and activation of TLRs in response to exogenous microbial insults or endogenous agents. We hypothesized that blocking MD2 using a specific inhibitor would prevent TLR4-mediated inflammatory responses and metastatic cancer growth. Here, we report that a MD2 inhibitor, L6H21, inhibited migration and invasion of LPS-activated colon cancer CT26.WT cells. These activities were accompanied by inhibition of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation, and thereby inhibition of the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and adhesive molecules in colon cancer cells. Furthermore, L6H21 inhibited CT26.WT metastasis to the lung in BALB/c mice as well as suppressed colitis-induced colon cancer induced by azoxymethane/dextran sulfate sodium (AOM/DSS). Taken together, our results demonstrated that L6H21 suppressed tumor invasion and metastasis through blocking TLR4-MD2/NF-κB signaling axis. These findings reveal that inhibition of MD2 may be an important target for the development of colon cancer therapies.
Keywords: colon cancer, MD2, TLR4, NF-κB, colitis-induced colon cancer

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact