ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(11):1785-1797. doi:10.7150/ijbs.39046 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Diagnostic, progressive and prognostic performance of m6A methylation RNA regulators in lung adenocarcinoma
1. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children's Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325000, Zhejiang Province, China.
2. Department of Pharmacy, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310000, China.
3. Second clinical college of medicine, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325000, Zhejiang Province, China.
4. Department of Respiratory medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children's Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325000, Zhejiang Province, China.
5. Department of Hematology and Medical Oncology, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children's Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325000, Zhejiang Province, China.
6. College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325000, Zhejiang Province, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
✉ Corresponding author: Yi Jin. Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children's Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325000, Zhejiang Province, China. Tel: +86-0577-88002611. E-mail: jinyi1990@wzhealth.com.
Abstract
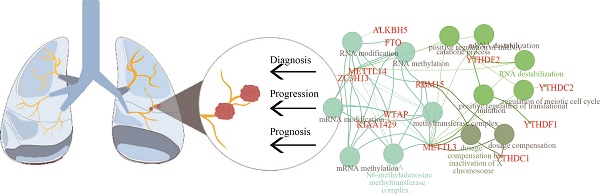
Background: N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA methylation is dynamically and reversibly regulated by methyl-transferases ("writers"), binding proteins ("readers"), and demethylases ("erasers"). The m6A is restored to adenosine and thus to achieve demethylation modification. The abnormality of m6A epigenetic modification in cancer has been increasingly attended. However, we are rarely aware of its diagnostic, progressive and prognostic performance in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD).
Methods and Results: The expression of 13 widely reported m6A RNA regulators in LUAD and normal samples were systematically analyzed. There were 12 m6A RNA methylation genes displaying aberrant expressions, and an 11-gene diagnostic score model was finally built (Diagnostic score =0.033*KIAA1429+0.116*HNRNPC+0.115*RBM15-0.067* METTL3-0.048*ZC3H13-0.221*WTAP+0.213*YTHDF1-0.132*YTHDC1-0.135* FTO+0.078*YTHDF2+0.014*ALKBH5). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed to demonstrate superiority of the diagnostic score model (Area under the curve (AUC) was 0.996 of training cohort, P<0.0001; AUC was 0.971 of one validation cohort-GSE75037, P<0.0001; AUC was 0.878 of another validation cohort-GSE63459, P<0.0001). In both training and validation cohorts, YTHDC2 was associated with tumor stage (P<0.01), while HNRNPC was up expressed in progressed tumor (P<0.05). Besides, WTAP, RBM15, KIAA1429, YTHDF1, and YTHDF2 were all up expressed for TP53 mutation. Furthermore, using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (lasso) regression analysis, a ten-gene risk score model was built. Risk score=0.169*ALKBH5-0.159*FTO+0.581*HNRNPC-0.348* YTHDF2-0.265*YTHDF1-0.123*YTHDC2+0.434*RBM15+0.143*KIAA1429-0.200*WTAP-0.310*METTL3. There existed correlation between the risk score and TNM stage (P<0.01), lymph node stage (P<0.05), gender (P<0.05), living status (P<0.001). Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses of relevant clinicopathological characters and the risk score revealed risk score was an independent risk factor of lung adenocarcinoma (HR: 2.181, 95%CI (1.594-2.984), P<0.001). Finally, a nomogram was built to facilitate clinicians to predict outcome.
Conclusions: m6A epigenetic modification took part in the progression, and provided auxiliary diagnosis and prognosis of LUAD.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine, diagnostic score model, risk score, clinicopathological characters, lung adenocarcinoma

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact