10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(13):2392-2404. doi:10.7150/ijbs.47035 This issue Cite
Research Paper
LEF1/Id3/HRAS axis promotes the tumorigenesis and progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
1. Department of Thoracic Surgery, Changhai Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200433, China;
2. Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Changhai Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200433, China.
*Authors contributed equally to this manuscript.
Abstract
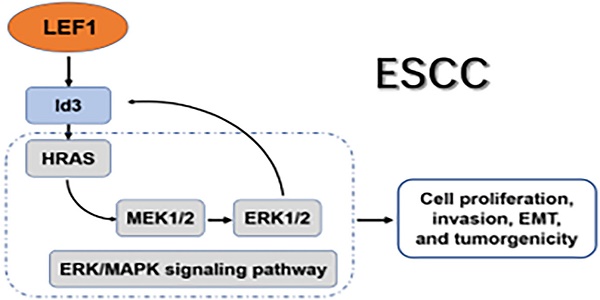
Our previous study demonstrated that lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (LEF1) could promote the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). However, the regulatory mechanism of LEF1 was not clear thoroughly. Herein, we continued to explore the downstream mechanism of LEF1 in ESCC. In this study, we applied western blotting, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), immunohistochemistry, RNA-Seq analysis, a luciferase reporter assay, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), bioinformatics analysis, and a series of functional assays in vitro and in vivo. The results demonstrated that LEF1 regulated directly the expression of Id3. Id3 was highly expressed in ESCC tissues and correlated with histologic differentiation (p=0.011), pT stage (p<0.01) and AJCC stage (p<0.01) in ESCC patients. Moreover, Id3 could serve as a prognostic factor of ESCC. By various functional experiments, overexpression of Id3 promoted the proliferation, migration, invasion, EMT, and tumorgenicity. Mechanistically, Id3 could regulate ERK/MAPK signaling pathway via activating HRAS to perform its biological function. Furthermore, activating ERK/MAPK signaling pathway promoted the expression of Id3 gene in turn, indicating that a positive regulatory loop between Id3 and ERK/MAPK pathway may exist in ESCC. In summary, LEF1/Id3/HRAS axis could promote the tumorigenesis and progression of ESCC via activating ERK/MAPK signaling pathway. Targeting this cascade may provide a valid antitumor strategy to delay ESCC progress.
Keywords: LEF1, Id3, HRAS, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, MAPK signaling pathway.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact