10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(14):2542-2558. doi:10.7150/ijbs.45446 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Cancer-associated Fibroblasts induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Transglutaminase 2-dependent IL-6/IL6R/STAT3 axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1. Cell-gene Therapy Translational Medicine Research Center, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China.
2. Guangdong Key Laboratory of Liver Disease Research, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China.
3. Department of Hepatic Surgery and Liver transplantation Center of the Third Affiliated Hospital, Organ Transplantation Institute, Sun Yat-sen University; Organ Transplantation Research Center of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou, China.
4. Department of medical oncology, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China.
5. Department of pathology, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China.
6. Zhongshan School of Medicine, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China.
7. School of Informatics, computing and engineering, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN, USA.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
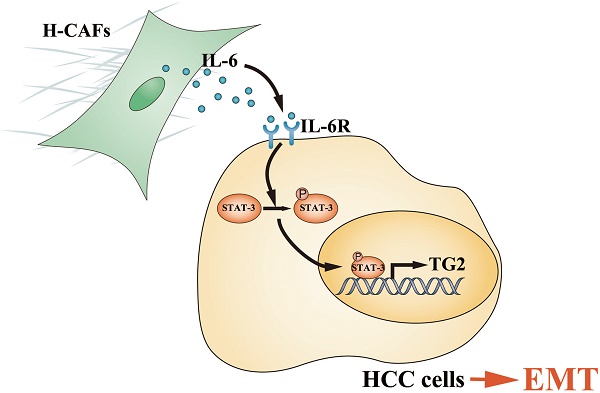
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) play crucial roles in enhancing cell survival, proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. We previously showed that hepatocellular carcinoma-derived CAFs (H-CAFs) promoted proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. This study aimed to further explore the role of CAFs in HCC epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and the underlying mechanism. High CAF density was significantly associated with liver cirrhosis, inferior clinicopathologic characteristics, elevated EMT-associated markers, and poorer survival in human HCC. Within HCC cells, EMT was induced after co-culture with H-CAFs. Secretomic analysis showed that IL-6 and HGF were the key EMT-stimulating cytokines secreted by H-CAFs. Proteomic analysis revealed that TG2 was significantly upregulated in HCC cells with EMT phenotypes. Overexpression of TG2 promoted EMT of HCC cells, and knockdown of TG2 remarkably attenuated the H-CAF-induced EMT. Furthermore, during EMT, TG2 expression was enhanced after HCC cells were stimulated by IL-6, but not HGF. Inhibition of the IL-6/STAT3 signaling decreased TG2 expression. The principal TG2 transcription control element and a potential STAT3 binding site were identified using promoter analysis. Hence, H-CAFs facilitates HCC cells EMT mediated by IL-6, which in turn activates IL-6/IL6R/STAT3 axis to promote TG2 expression.
Keywords: HCC, CAFs, EMT, TG2, IL-6/IL6R/STAT3 axis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact