10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(2):390-401. doi:10.7150/ijbs.53872 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Spreading of pathological TDP-43 along corticospinal tract axons induces ALS-like phenotypes in Atg5+/- mice
1. Department of Neurology, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, 410008, China
2. The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, 450052, China
3. Institute of Parkinson and Movement Disorder, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, 450052, China
4. Neuroscience Institute and Department of Neurosurgery, Baylor Scott & White Health, Temple, Texas, 76508, USA
5. College of Medicine, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, 77843, USA
6. Irma Lerma Rangel College of Pharmacy, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, 77843, USA
7. LIVESTRONG Cancer Institutes and Department of Oncology, Dell Medical School, the University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, 78712, USA
8. Academy of Medical Sciences, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, 450052, China
Abstract
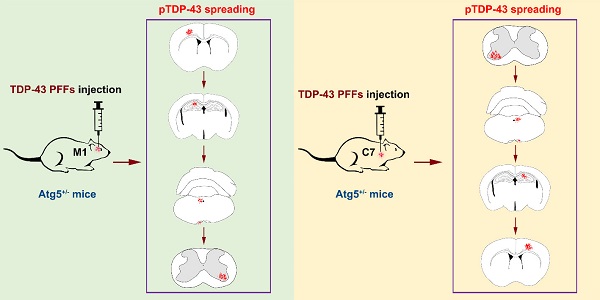
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease, characterized by phosphorylated TDP-43 (pTDP-43)-positive inclusions in neurons and glial cells. However, the pathogenic mechanism that underlies ALS remains largely unknown. To investigate the effects of autophagy deficiency in the formation and spreading of pathological TDP-43 along corticospinal tract axons, TDP-43 preformed fibrils (PFFs) were prepared and unilaterally injected into the fifth layer of the left primary motor cortex (M1) or the left anterior horn of the seventh cervical spinal cord segment (C7) of Atg5+/- mice. After the injection of TDP-43 PFFs, the elevated levels of pTDP-43 were present in several pyramidal tract-associated regions of Atg5+/- mice. Additionally, the occurrence of spontaneous potentials detected by electromyography demonstrates evidence of lower motor neuron dysfunction in M1-TDP-43 PFFs-injected Atg5+/- mice, and prolonged central motor conduction time detected by motor evoked potentials provides evidence of upper motor neuron dysfunction in C7-TDP-43 PFFs-injected Atg5+/- mice. These results show that injection of TDP-43 PFFs into the M1 or C7 of Atg5+/- mice induces the spreading of pathological TDP-43 along corticospinal tract axons in both an anterograde and retrograde manner. Importantly, TDP-43 PFFs-injected Atg5+/- mice also display ALS-like motor dysfunction. Taken together, our findings provide direct evidence that TDP-43 PFFs-injected Atg5+/- mice exhibited ALS-like neuropathology and motor phenotypes, suggesting that autophagy deficiency promotes the formation and spreading of pathological TDP-43 in vivo.
Keywords: TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), autophagy, preformed fibrils (PFFs), Atg5+/- mice

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact