10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(2):402-416. doi:10.7150/ijbs.53419 This issue Cite
Review
The role of miR-320 in glucose and lipid metabolism disorder-associated diseases
Division of Cardiology, Hubei Key Laboratory of Genetics and Molecular Mechanisms of Cardiological Disorders, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430030, China
Abstract
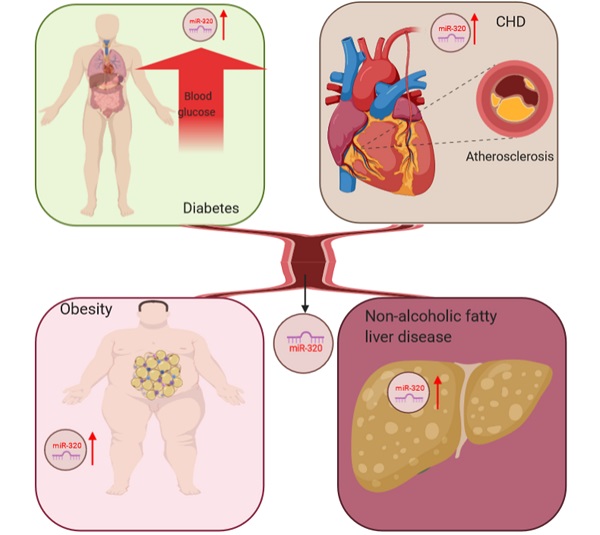
Glucose and lipids are important nutrients that provide the majority of energy for each organ to maintain homeostasis of the body. With the continuous improvement in living standards, the incidence of metabolic disorder-associated diseases, such as diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and atherosclerosis, is increasing worldwide. Among them, diabetes, which could be induced by both glucose and lipid metabolic disorders, is one of the five diseases with the highest incidence and mortality worldwide. However, the detailed molecular mechanisms underlying glucose and lipid metabolism disorders and target-organ damage are still not fully defined. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding, single-stranded RNAs, which usually affect their target mRNAs in the cytoplasm by post-transcriptional regulation. Previously, we have found that miR-320 contributed to glucose and lipid metabolism via different signaling pathways. Most importantly, we identified that nuclear miR-320 mediated diabetes-induced cardiac dysfunction by activating the transcription of fatty acid metabolic genes to cause lipotoxicity in the heart. Here, we reviewed the roles of miR-320 in glucose and lipid metabolism and target-organ damage.
Keywords: miRNA, glucose and lipid metabolism, diseases

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact