Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(3):702-711. doi:10.7150/ijbs.55552 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Ferroptosis-Related Long Non-Coding RNA signature predicts the prognosis of Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
1. Department of Critical Care Medicine, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430022, China.
2. Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, The Central Hospital of Wuhan, Tongji Medical College Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China.
3. School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and technology, Wuhan, China.
4. Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China.
5. Department of Infectious Diseases, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China.
Abstract
Background: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) are head and neck cancers. On the other hand, ferroptosis is a novel iron-dependent and ROS reliant type of cell death observed various disease conditions.
Method: We constructed a prognostic multilncRNA signature based on ferroptosis-related differentially expressed lncRNAs in HNSCC.
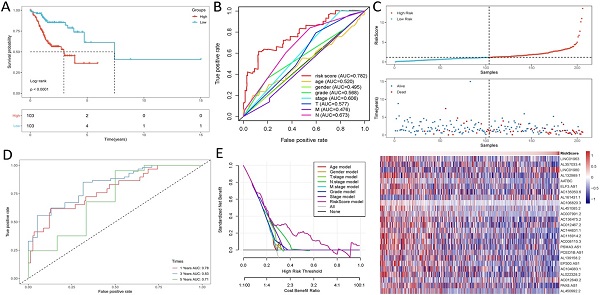
Results: We identified 25 differently expressed lncRNAs associated with prognosis of HNSCC. Kaplan-Meier analyses revealed the high-risk lncRNAs signature associated with poor prognosis of HNSCC. Moreover, the AUC of the lncRNAs signature was 0.782, underscoring their utility in prediction HNSCC prognosis. Indeed, our risk assessment model was superior to traditional clinicopathological features in predicting HNSCC prognosis. GSEA revealed the immune and tumor-related pathways in the low risk group individuals. Moreover, TCGA revealed T cell functions including cytolytic activity, HLA, regulation of inflammationp, co-stimulation, co-inhibition and coordination of type II INF response were significantly different between the low-risk and high-risk groups. Immune checkpoints such as PDCD-1 (PD-1), CTLA4 and LAG3, were also expressed differently between the two risk groups.
Conclusion: A novel ferroptosis-related lncRNAs signature impacts on the prognosis of HNSCC.
Keywords: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, ferroptosis, genes, lncRNAs, immune infiltration, data mining.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact