10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(3):818-833. doi:10.7150/ijbs.56214 This issue Cite
Review
Understanding the Effects of Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Possible Probiotics Role: Recent Updates
1. School of Life Sciences, Probiotics and Biological Feed Research Centre, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, PR China.
2. Department of Microbiology, Balochistan University of Information Technology Engineering & Management Sciences Quetta 87300, Pakistan.
3. School of Life Sciences, Institute of Microbiology Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, PR China.
Abstract
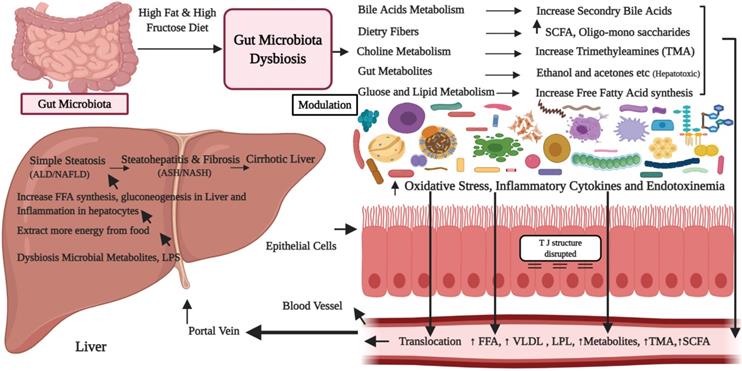
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is leading chronic liver syndrome worldwide. Gut microbiota dysbiosis significantly contributes to the pathogenesis and severity of NAFLD. However, its role is complex and even unclear. Treatment of NAFLD through chemotherapeutic agents have been questioned because of their side effects on health. In this review, we highlighted and discussed the current understanding on the importance of gut microbiota, its dysbiosis and its effects on the gut-liver axis and gut mucosa. Further, we discussed key mechanisms involved in gut dysbiosis to provide an outline of its role in progression to NAFLD and liver cirrhosis. In addition, we also explored the potential role of probiotics as a treatment approach for the prevention and treatment of NAFLD. Based on the latest findings, it is evident that microbiota targeted interventions mostly the use of probiotics have shown promising effects and can possibly alleviate the gut microbiota dysbiosis, regulate the metabolic pathways which in turn inhibit the progression of NAFLD through the gut-liver axis. However, very limited studies in humans are available on this issue and suggest further research work to identify a specific core microbiome association with NAFLD and to discover its mechanism of pathogenesis, which will help to enhance the therapeutic potential of probiotics to NAFLD.
Keywords: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, gut microbiota, probiotics, dysbiosis, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact